Garra typhlops
(Bruun and Kaiser 1944) Farashi, Kaboli, Rezaei, Naghavi, Rahimian and Coad 2014
| ORDER | SUB-ORDER | FAMILY |
|---|---|---|
| Cypriniformes | Cyprinoidei | Cyprinidae |
Note
Notes on subterranean Garra species in West Asia (Freyhof et al. 2025)
Garras in West Asia. Since their discovery, the troglomorphic animals, adapted to live in subterranean habitats, have fascinated humans. The most striking features of many troglobionts (cave-dwelling species) are the reduction of eyes and pigmentation. The discussion about the forces driving convergent evolution of reduced eyes and loss of pigmentation in typical cave-living animals was initiated very early in the history of evolutionary theory. It is usually attributed to subterranean animals’ access to very limited resources and their need to save energy. The loss of pigmentation and eyes provides an advantage by conserving energy. In West Asia, six species of Garra have entered cave and underground waters, while only three other fish species did so (the cyprinid Caecocypris basimi and the loaches Eidinemacheilus smithi and E. proudlovi). It can be hypothesised that species of Garra are preadapted to subterranean life. A study on the eye morphology of G. rufa suggests that it has limited eyesight. Furthermore, Garra species are already adapted to grazing algae and other biofilms from surfaces and possess a long and coiled gut, which allows them to digest food effectively. In underground habitats, food resources are likely to be very restricted, and fishes that can graze bacteria- and ciliate-dominated biofilms from surfaces might not encounter the same challenges as other fish species may face regarding food scarcity. In light of this advantage, cave Garra may have adapted relatively quickly to the new environment by reducing their eye, colour, and scales, which are not as necessary in such a predator-free environment. Further reading. Romero and Paulson 2001 (subterranean fishes); Kruckenhauser et al. 2011; Kirchner et al. 2017 (molecular studies on Omani cave Garra)
Synonyms
Iranocypris typhlops Bruun and Kaiser 1944
Country
IranTypes
Holotype: ZMUC P26475 38.0mm SL. Paratypes ZMUC P26476-80 16.5mm - 34.5mm SL (5 specimens). This species is the type species by original designation and monotypy of the cave-restricted genus Iranocypris.
Distribution
Type locality: a flood resurgence at Kaaje‑Ru, near the oasis of Baq‑e‑Loveh, Lorestan Province, Zagros Mountains, Iran ( 33°04'39"N, 48°35'33"E.). This locality is 11 km from Tanh‑e‑kraft railway station on the line from Bendar Shapur to Tehran. This is also the type (and only known) locality of Garra lorestanensis and Eidinemacheilus smithi and the three species coexist. A second flooded cave is found 50m distant from the original and is likely an opening into the same phreatic cave. Known also from Tuveh Spring in the Dez River drainage 31km from the type locality (Vatandoust et al. 2019).
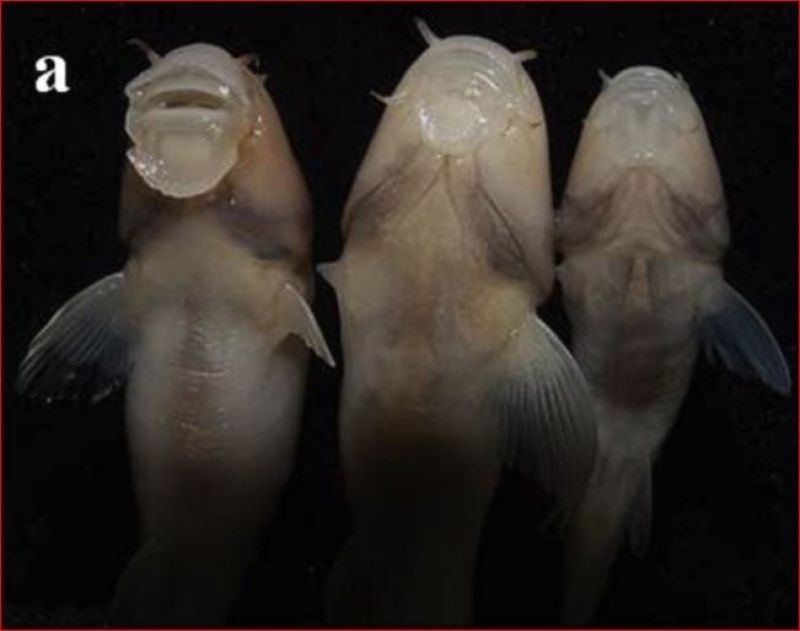
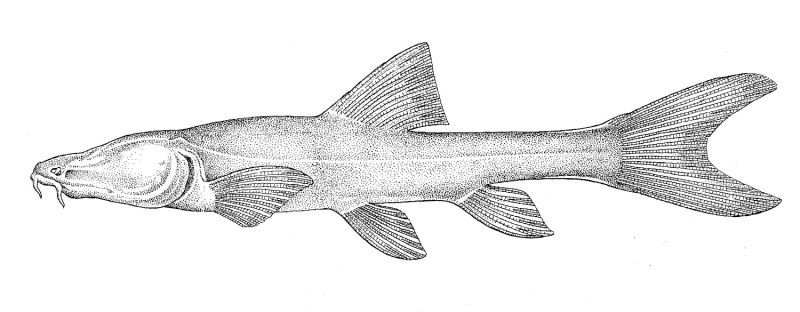
A report by Mahjoorazad and Coad (2009) suggests that G. typhlops has been collected in cave 130km distant from the type locailty, and that the species is distributed across the Zagros Mountains, should surely be dismissed. It is exceedingly unlikely that a single panmictic population of a subterranean fish could exist over such a huge area as karst terrains, and particularly the sink to resurgence flow paths, are highly fragmented. The null hypothesis for this second location is that it is an entirely separate species of Garra. The cave it was found in is no longer accessible. Mahjoorazad and Coad (2009) report that the fish at the remote location had a mental disk and if this is so it could not be G. typhlops which is without a disk (Figure a, below).
Habitat
The true habitat of this species is not known. The collection site is the flood overflow for a large resurgence. The resurgence was explored by diving (Farr 1977, 1984:117) but the way on underwater became too narrow at 2m depth. The flood overflow was also dived but without conclusion. Another sump is located in the same area but was not examined (Farr 1977).
Systematics
Garra typhlops is a member of the monophyletic group termed labeine cyprinids by Reid (1978, 1982). This comprises 13 genera defined by four synapomorphies. The cave restricted species Garra widdowsoni and Garra barreimiae are also members of this group. Howes (1991) places the labeine assemblage in the subfamily Cyprininae.
It has been known since 2008 (Sargeran et al. 2008) that some of the fishes at the type locailty have a mental disk while others do not (Figure a, below). Hashemzadeh Segherloo et al. (2012) used cytochrome c oxidase I (coI ) sequences for the two morphological forms. They concluded that "Pronounced coI sequence divergence between the two forms of I. typhlops (3·8% K2P distance) was observed. This sequence divergence is higher than the mean intraspecific divergence values reported in other taxa, e.g.0·46% in Lepidoptera, 0·60% in Guyanese bats, 0·27% in North American birds, 0·39% in marine fishes and 0·27% K2P distance in freshwater fishes. The high sequence divergence between the two forms, along with the morphological differences, including the presence of a mental disc, the longer intestine, and either a single chambered or bipartite swimbladder in the specimens with disc, v. the absence of the mental disc, shorter intestine and bipartite swimbladder in the second form, as reported by Sargeran et al. (2008), indicate that the two forms might represent separate species" (Hashemzadeh Segherloo et al. 2012). But they did not go so far as to state that two species were actually present nor to describe the second one. They also showed that the two cave forms are close to Garra rufa.
Farashi et al (2014), still assuming that the two forms were the same species (Iranocypris typhlops), used mitochondrial cytochrome b sequences and concluded that the species was close to the genus Garra and recommended that Iranaocypris typhlops should be transferred to the genus Garra Hamilton, 1822.
It was not until 2016 (Mousavi-Sabet and Eagderi 2016) that the second and most recently discovered form (the form with a mental disc) was described as a separate species to Garra typhlops. It was named Garra lorestanensis.
Most recently Hashemzadeh Segherloo et al. (2018), using a mixture of molecular markers, showed that G. typhlops and G. lorestanensis were sister species and that both were sister to the geographically close Garra gymnothorax. The evidence suggets that the two cave species evolved by sympatric speciation. A mitochondria divergence of 3.6% between the two cave species suggest a divergence time of 5-6 million years.
Zamani-Faradonbe et al. (2021) found a different topology. Their data make G. typhlops sister to a group containing G. tiam, G. meymehensis and G. gymnothorax. The sister to this group is G. lorestanensis.
Jalili and Eagderi (2014) examined the osteology of what they called Iranocypris typhlops (now Garra typhlops). However, the three specimens used in their study each had a mental disk so were, in fact, Garra lorestanensis.
Conservation Status
R (IUCN 1990), R (IUCN 1994). B. Sandford (in Coad 1980-81:73) considers that this species (and its co-inhabitants Garra lorestanensis and Eidinemacheilus smithi) should be considered endangered because of a collapse at the resurgence from which they were collected. However, as Coad points out (1980-81:72-73), these species may not be threatened since the pool in which they were collected probably represents only a small and atypical portion of their habitat. The cave or fissure system in which they have evolved and now live may be quite extensive. Furthermore it is in a very remote area which is unlikely to be threatened by pollution, disturbance, or habitat destruction, at least for some time. See also Coad (1996). The population size was assessed by Bagheri et al. (2016), using a Peterson and Schnabel mark-recapture sampling during an 8-day period in 2010, at 300 to 600 individuals.
Museum Holdings
As above plus: BMNH 1977.5.19:1, BMNH 1979.6.15:1-2. NMC uncatalogued 8 specimens (Brian Coad pers. comm.). VMFC GT01, VMFC GT02 to VMFC GT07, VMFC GT08 to VMFC GT10 (Mousavi-Sabet and Eagderi 2016).
Internet Resources
Brian Coad's freshwater fishes of Iran website
Osteological description of Garra typhlops (Jalili and Eagderi 2014)
Garra typhlops COI (1) (Hamidan et al. 2014)
Garra typhlops COI (2) (Hashemzadeh Segherloo et al. 2012)
Garra typhlops COI (3) (Hashemzadeh Segherloo et al. 2018)
Key References
- Bruun, A. F. and Kaiser, E. W. (1944)
- Smith, A. (1953)
- Movaghar, S. (1973)
- Greenwood, P. H. (1976)
- Anonymous (1976)
- Smith, A. (1977)
- Farr, M. J. (1977)
- Thines, G. (1978)
- Smith, A. (1978)
- Reid, G. McG. (1978)
- Smith, A. (1979)
- Coad, B.W. (1980-81)
- Reid, G. McG. (1982)
- Farr, M. J. (1984)
- Coad, B.W. (1987)
- Smith, A. (1990)
- Coad, B.W. (1996)
- Juberthie, C., Decu, V. and Povara, I. (2001)
- Smith, A. (2004)
- Coad, B.W. and Vilenkin, B.Y. (2004)
- Coad, B.W. (2005)
- Sargeran, P., Bakhttiyari, M., Abdoli, A., Coad, B.W., Sarvi, K., Lishi, M.R. and Hajimoradloo, A. (2008)
- Abbasi, M. and Gharezi A. (2008)
- Coad, B.W., Mehrani, R. and Najafpour, N. (2009)
- Mahjoorazad, A. and Coad, B.W. (2009)
- Coad, B.W. (2009)
- Esmaeili, H.R., Coad, B.W., Gholamifard, A., Nazari, N. and Teimory, A. (2010)
- Gharzi, A. Ebrahimi Bagheban, A. and Abbasi, M. (2011)
- Raeisi, E., and Laumanns, M. (2012)
- Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I, Bernatchez, L, Golzarianpour, K., Abdoli, A, Primmer, C. R. and Bakhtiary, M. (2012)
- Mousavi-Sabet, H. (2013)
- Esmaeilzadegan, E. (2013)
- Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Rahmati, S., Purahmad, R., Golzarianpour, K. and Abdoli A. (2013)
- Farashi, A., Kaboli, M., Rezaei, H.R., Naghavi, M.R., Rahimian, H. and Coad, B.W. (2014)
- Jalili, P and Eagderi, S (2014)
- Farashi, A., Kaboli, M., Rezaei, H.R., Naghavi, M.R. and Rahimian, H. (2014)
- Jouladeh-Roudbar, A., Vatandoust, S., Eagderi, S., Jafari-Kenari, S. and Mousavi-Sabet, H. (2015)
- Farashi, A., Kaboli, M., Rahimian, H., Rezaei, H. R. and Naghavi, M. R. (2015)
- Sayyadzadeh, G., Esmaeili, H.R. and Freyhof, J. (2015)
- Ebrahimi, A. (2015)
- Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Ghaedrahmati, N. and Freyhof, J. (2016)
- Mousavi-Sabet, H. and Eagderi, S. (2016)
- Bagheri, M., Goudarzi, F., Zalaghi, A.H. and Savabieasfahani, M. (2016)
- Mousavi-Sabet, H., Vatandoust, S., Fatemi, Y. and Eagderi, S. (2016)
- Teimori, A., Mostafavi, H. and Esmaeli, H.R. (2016)
- Esmaeili, H.R., Sayyadzadeh, G., Coad, B.W. and Eagderi, S. (2016)
- Nebeshwar, K and Vishwanath, W (2017)
- Esmaeili, H.R., Mehraban, H., Abbasi, K., Keivany, Y. and Coad, B. (2017)
- Vardanjani, H.K., Bahadorinia, S. and Ford, D.C. (2017)
- Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Abdoli, A., Eagderi, S., Esmaeili, H.R., Sayyadzadeh, G., Bernatchez, L., Hallerman, E., Geiger, M.F., Ozulug, M., Laroche, J. and Freyhof, J. (2017)
- Malek-Hosseini, M.J. and Zamani, A. (2017)
- Coad, B.W. (2017)
- Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Normandeau, E., Benestan, L., Rougeux, C., Cote, G. Moore, J.-S., Ghaerahmati, N.A., Abdoli, A. and Bernatchez, L. (2018)
- Khalaji-Pirbalouty, V., Fatemi, Y., Malek-Hosseini, M.J. and Kuntner, M. (2018)
- Esmaeili, H.R., Sayyadzadeh, G., Eagderi, S. and Abbasi, K. (2018)
- Vatandoust, S., Mousavi‐Sabet, H., Geiger, M.F. and Freyhof, J. (2019)
- Fatemi, Y., Malek Hosseini, M.-J., Falniowski, A., Hofman, S., Kuntner, M. and Grego, J. (2019)
- Barmaki, M.D., Rezaei, M., Raeisi, C.E. and Ashjari, J. (2019)
- Hashemzadeh, I., Tabatabaei, S.N., Ghaed Rahmati, N., Amiri, M. and Bernatchez, L. (2020)
- Saemi-Komsari, M., Mousavi-Sabet, H., Sattari, M., Eagderi, S., Vatandoust, S. and Doadrio, I. (2020)
- Sungur, S., Eagderi, S., Jalili, P. and Cicek, E. (2020)
- Jouladeh-Roudbar, A., Ghanavi, H.R. and Doadrio, I. (2020)
- Zamanpoore, M. (2021)
- Freyhof, J., Kaya, C. and Ali, A. (2021)
- Zamani-Faradonbe, M. and Keivany, Y. (2021)
- Zamani-Faradonbe, M., Zhang, E. and Keivany, Y. (2021)
- Ashraf, S., Nazemi, A. and AghaKouchak, A. (2021)
- Zamani-Faradonbe, M., Keivany, Y., Dorafshan, S. and Zhang, E. (2021)
- Zamani-Faradonbe M. and Keivany Y. (2021)
- Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Tabatabaei, S.N., Abdolahi-Mousavi, E., Hernandez, C., Normandeau, E., Laporte, M., Boyle, B., Amiri, M., GhaedRahmati, N., Hallerman, E. and Bernatchez, L. (2022)
- Malek-Hosseini, M.J., Jugovic, J., Fatemi, Y., Kuntner, M., Kostanjšek, R., Douady, C.J. and Malard, F. (2022)
- Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Najafi Chaloshtory, S., Naser, M.D., Yasser, A.G., Tabatabaei, S.N., Piette‑Lauziere, G., Mashtizadeh, A., Elmi, A., Sedighi, O., Changizi, A., Hallerman, E. and Bernatchez (2022)
- Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Najafi Chaloshtory, S., Naser, M.D., Yasser, A.G., Tabatabaei, S.N., Piette‑Lauziere, G., Mashtizadeh, A., Elmi, A., Sedighi, O., Changizi, A., Hallerman, E. and Bernatchez, L. (2022)
- Yousefi, M., Jouladeh-Roudbar, S. and Kafash, A. (2023)
- Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Najafi Chaloshtory, S., Yasser, A.G., Naser, M.D., Normandeau, E., Mashtizadeh, A., Elmi, A., Sedighi, O., Changizi, A., Hallerman, E. and Bernatchez, L. (2023)
- Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Abdolahi‑Mousavi, S.E., Birgani, A.A., Normandeau, E., Hallerman, E., Bernatchez, L. and Freyhof, J. (2024)
- Freyhof, J., Yoğurtçuoğlu, B., Jouladeh-Roudbar, A. and Kaya, C. (2025)
| Bruun, A. F. and Kaiser, E. W. | Journal Article | 1944 | Iranocypris typhlops n.g., n. sp., the first true cave fish from Asia |
| Smith, A. | Book | 1953 | Blind white fish in Persia |
| Movaghar, S. | Journal Article | 1973 | Iranocypris typhlops Kaiser the blind cave fish from Iran |
| Greenwood, P. H. | Journal Article | 1976 | A new and eyeless cobitid fish (Pisces, Cypriniformes) from the Zagros Mountains, Iran |
| Anonymous | Journal Article | 1976 | The blind white fishes of Persia |
| Smith, A. | Journal Article | 1977 | Blind white fish discovery |
| Farr, M. J. | Journal Article | 1977 | Karue Ru Resurgence, Zagros Mountains, Iran |
| Thines, G. | Journal Article | 1978 | The blind fishes of Persia |
| Smith, A. | Journal Article | 1978 | The blind fishes of Persia |
| Reid, G. McG. | Thesis | 1978 | A sytematic study of labeine cyprinid fishes with particular reference to the comparative morphology, functional morphology and morphometrics of African Labeo species |
| Smith, A. | Book | 1979 | A Persian quarter century |
| Coad, B.W. | Journal Article | 1980-81 | Environmental change and its impact on the freshwater fishes of Iran |
| Reid, G. McG. | Journal Article | 1982 | The form, function and phylogenetic significance of the vomero-palatine organ in Cyprinid fishes |
| Farr, M. J. | Book | 1984 | The great caving adventure |
| Coad, B.W. | Journal Article | 1987 | Zoogeography of the freshwater fishes of Iran |
| Smith, A. | Book | 1990 | Blind white fish in Persia. 2nd edition |
| Coad, B.W. | Journal Article | 1996 | Threatened fishes of the world: Iranocypris typhlops Bruun and Kaiser, 1944 (Cyprinidae) |
| Juberthie, C., Decu, V. and Povara, I. | Book Section | 2001 | Iran |
| Smith, A. | Journal Article | 2004 | [Corresponence re cave fishes in Iran and Iraq] |
| Coad, B.W. and Vilenkin, B.Y. | Journal Article | 2004 | Co-occurence and zoogeography of the freshwater fishes of Iran |
| Coad, B.W. | Journal Article | 2005 | Endemicity in the freshwater fishes of Iran |
| Sargeran, P., Bakhttiyari, M., Abdoli, A., Coad, B.W., Sarvi, K., Lishi, M.R. and Hajimoradloo, A. | Journal Article | 2008 | The endemic Iranian cave-fish, Iranocypris typhlops: Two taxa or two forms based on the mental disk? |
| Abbasi, M. and Gharezi A. | Journal Article | 2008 | Morphology and histology of the digestive tract of Iranian blind cave fish (Iranocypris typhlops) |
| Coad, B.W., Mehrani, R. and Najafpour, N. | Journal Article | 2009 | Threatened fishes of the world: Paracobitis smithi (Greenwood, 1976) (Balitoridae) |
| Mahjoorazad, A. and Coad, B.W. | Journal Article | 2009 | A new cave fish locality for Iran |
| Coad, B.W. | Journal Article | 2009 | Criteria for assessing the conservation status of taxa (as applied to Iranian freshwater fishes) |
| Esmaeili, H.R., Coad, B.W., Gholamifard, A., Nazari, N. and Teimory, A. | Journal Article | 2010 | Annotated сhecklist of the freshwater fishes of Iran |
| Gharzi, A. Ebrahimi Bagheban, A. and Abbasi, M. | Journal Article | 2011 | Histomorphometry of urogenital system in Iranian cave barb (Iranocypris typhlops) |
| Raeisi, E., and Laumanns, M. | Book | 2012 | Cave Directory of Iran: 3rd edition |
| Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I, Bernatchez, L, Golzarianpour, K., Abdoli, A, Primmer, C. R. and Bakhtiary, M. | Journal Article | 2012 | Genetic differentiation between two sympatric morphs of the blind Iranian cave barb Iranocypris typhlops |
| Mousavi-Sabet, H. | Journal Article | 2013 | The Iran's blind cave fish Iranocycpris typhlops |
| Esmaeilzadegan, E. | Thesis | 2013 | Comparison of morphological characteristics of the sang-lis (Garra ruffa) and Iranian cave fish (Iranocypris typhlops). |
| Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Rahmati, S., Purahmad, R., Golzarianpour, K. and Abdoli A. | Journal Article | 2013 | Analysis of the systematic status of the blind Iran cave barb, Iranocypris typhlops, using COI gene. |
| Farashi, A., Kaboli, M., Rezaei, H.R., Naghavi, M.R., Rahimian, H. and Coad, B.W. | Journal Article | 2014 | Reassessment of the taxonomic position of Iranocycpris typhlops Bruun and Kaiser, 1944 (Actinopterygii: Cyprinidae) |
| Jalili, P and Eagderi, S | Journal Article | 2014 | Osteological description of Iran cave barb (Iranocypris typhlops Bruun and Kaiser, 1944) |
| Farashi, A., Kaboli, M., Rezaei, H.R., Naghavi, M.R. and Rahimian, H. | Journal Article | 2014 | Plankton composition and environmental parameters in the habitat of the Iranian cave barb (Iranocypris typhlops) in Iran |
| Jouladeh-Roudbar, A., Vatandoust, S., Eagderi, S., Jafari-Kenari, S. and Mousavi-Sabet, H. | Journal Article | 2015 | Freshwater fishes of Iran: An updated checklist |
| Farashi, A., Kaboli, M., Rahimian, H., Rezaei, H. R. and Naghavi, M. R. | Journal Article | 2015 | Selecting suitable habitat for Iranian blind fish (Iranocypris typhlops) |
| Sayyadzadeh, G., Esmaeili, H.R. and Freyhof, J. | Journal Article | 2015 | Garra mondica, a new species from the Mond River drainage with remarks on the genus Garra from the Persian Gulf basin in Iran |
| Ebrahimi, A. | Journal Article | 2015 | Study of the digestive tract of a rare species of Iranian blind cave fish (Iranocypris typhlops) |
| Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Ghaedrahmati, N. and Freyhof, J. | Journal Article | 2016 | Eidinemacheilus, a new generic name for Noemacheilus smithi Greenwood (Teleostei: Nemacheilidae) |
| Mousavi-Sabet, H. and Eagderi, S. | Journal Article | 2016 | Garra lorestanensis, a new cave fish from the Tigris River drainage with remarks on the subterranean fishes in Iran (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) |
| Bagheri, M., Goudarzi, F., Zalaghi, A.H. and Savabieasfahani, M. | Journal Article | 2016 | Habitat characteristics and population size of Iranocypris typhlops, the Iran cave barb |
| Mousavi-Sabet, H., Vatandoust, S., Fatemi, Y. and Eagderi, S. | Journal Article | 2016 | Tashan Cave a new cavefish locality for Iran; and Garra tashanensis, a new blind species from the Tigris River drainage (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) |
| Teimori, A., Mostafavi, H. and Esmaeli, H.R. | Journal Article | 2016 | An update note on diversity and conservation of the endemic fishes in Iranian inland waters |
| Esmaeili, H.R., Sayyadzadeh, G., Coad, B.W. and Eagderi, S. | Journal Article | 2016 | Review of the genus Garra Hamilton, 1822 in Iran with description of a new species: a morpho-molecular approach (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) |
| Nebeshwar, K and Vishwanath, W | Journal Article | 2017 | On the snout and oromandibular morphology of genus Garra, description of two new species from the Koladyne River basin in Mizoram, India, and redescription of G. manipurensis (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) |
| Esmaeili, H.R., Mehraban, H., Abbasi, K., Keivany, Y. and Coad, B. | Journal Article | 2017 | Review and updated checklist of freshwater fishes of Iran: Taxonomy, distribution and conservation status |
| Vardanjani, H.K., Bahadorinia, S. and Ford, D.C. | Book Section | 2017 | An introduction to hypogene karst regions and caves of Iran. |
| Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Abdoli, A., Eagderi, S., Esmaeili, H.R., Sayyadzadeh, G., Bernatchez, L., Hallerman, E., Geiger, M.F., Ozulug, M., Laroche, J. and Freyhof, J. | Journal Article | 2017 | Dressing down: convergent reduction of the mental disc in Garra (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) in the Middle East |
| Malek-Hosseini, M.J. and Zamani, A. | Journal Article | 2017 | A checklist of subterranean arthropods of Iran |
| Coad, B.W. | Web Page | 2017 | Freshwater fishes of Iran |
| Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Normandeau, E., Benestan, L., Rougeux, C., Cote, G. Moore, J.-S., Ghaerahmati, N.A., Abdoli, A. and Bernatchez, L. | Journal Article | 2018 | Genetic and morphological support for possible sympatric origin of fish from subterranean habitats |
| Khalaji-Pirbalouty, V., Fatemi, Y., Malek-Hosseini, M.J. and Kuntner, M. | Journal Article | 2018 | A new species of Stenasellus Dollfus, 1897 from Iran, with a key to the western Asian species (Crustacea, Isopoda, Stenasellidae) |
| Esmaeili, H.R., Sayyadzadeh, G., Eagderi, S. and Abbasi, K. | Journal Article | 2018 | Checklist of freshwater fishes of Iran |
| Vatandoust, S., Mousavi‐Sabet, H., Geiger, M.F. and Freyhof, J. | Journal Article | 2019 | A new record of Iranian subterranean fishes reveals the potential presence of a large freshwater aquifer in the Zagros Mountains |
| Fatemi, Y., Malek Hosseini, M.-J., Falniowski, A., Hofman, S., Kuntner, M. and Grego, J. | Journal Article | 2019 | Description of a new genus and species as the first gastropod species from caves in Iran |
| Barmaki, M.D., Rezaei, M., Raeisi, C.E. and Ashjari, J. | Journal Article | 2019 | Comparison of surface and interior karst development in Zagros karst Aaquifers, southwest Iran. |
| Hashemzadeh, I., Tabatabaei, S.N., Ghaed Rahmati, N., Amiri, M. and Bernatchez, L. | Journal Article | 2020 | The analysis of the relationship between Lorestan cave barbs (Garra typhlops and Garra lorestanensis) and Garra gymnothorax populations in Dez and Karkheh River drainages. |
| Saemi-Komsari, M., Mousavi-Sabet, H., Sattari, M., Eagderi, S., Vatandoust, S. and Doadrio, I. | Journal Article | 2020 | Descriptive osteology of Garra rossica (Nikolskii 1900) |
| Sungur, S., Eagderi, S., Jalili, P. and Cicek, E. | Journal Article | 2020 | Caudal osteology and its application to reconstruct phylogenetic relationship in the genus Garra |
| Jouladeh-Roudbar, A., Ghanavi, H.R. and Doadrio, I. | Journal Article | 2020 | Ichthyofauna from Iranian freshwater: Annotated checklist, diagnosis, taxonomy, distribution and conservation assessment |
| Zamanpoore, M. | Book Section | 2021 | Biodiversity of the freshwater Amphipods in Iran |
| Freyhof, J., Kaya, C. and Ali, A. | Book Section | 2021 | A critical checklist of the inland fishes native to the Euphrates and Tigris drainages |
| Zamani-Faradonbe, M. and Keivany, Y. | Journal Article | 2021 | Comparative osteology of two Garra species (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae) from Hormuz and Sistan basins of Iran |
| Zamani-Faradonbe, M., Zhang, E. and Keivany, Y. | Journal Article | 2021 | Garra hormuzensis, a new species from the upper Kol River drainage in the Persian Gulf basin (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) |
| Ashraf, S., Nazemi, A. and AghaKouchak, A. | Journal Article | 2021 | Anthropogenic drought dominates groundwater depletion in Iran |
| Zamani-Faradonbe, M., Keivany, Y., Dorafshan, S. and Zhang, E. | Journal Article | 2021 | Two new species of Garra (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) from western Iran |
| Zamani-Faradonbe M. and Keivany Y. | Journal Article | 2021 | Biodiversity and distribution of Garra species (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) in Iran |
| Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Tabatabaei, S.N., Abdolahi-Mousavi, E., Hernandez, C., Normandeau, E., Laporte, M., Boyle, B., Amiri, M., GhaedRahmati, N., Hallerman, E. and Bernatchez, L. | Journal Article | 2022 | eDNA metabarcoding as a means to assess distribution of subterranean fish communities: Iranian blind cave fishes as a case study |
| Malek-Hosseini, M.J., Jugovic, J., Fatemi, Y., Kuntner, M., Kostanjšek, R., Douady, C.J. and Malard, F. | Journal Article | 2022 | A new obligate groundwater species of Asellus (Isopoda, Asellidae) from Iran |
| Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Najafi Chaloshtory, S., Naser, M.D., Yasser, A.G., Tabatabaei, S.N., Piette‑Lauziere, G., Mashtizadeh, A., Elmi, A., Sedighi, O., Changizi, A., Hallerman, E. and Bernatchez | Journal Article | 2022 | Sympatric morphotypes of the restricted‑range Tashan Cave Garra: distinct species or a case of phenotypic plasticity? |
| Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Najafi Chaloshtory, S., Naser, M.D., Yasser, A.G., Tabatabaei, S.N., Piette‑Lauziere, G., Mashtizadeh, A., Elmi, A., Sedighi, O., Changizi, A., Hallerman, E. and Bernatchez, L. | Journal Article | 2022 | Two different mental disc forms in the Tashan cave Garra: different species or ecotypes? |
| Yousefi, M., Jouladeh-Roudbar, S. and Kafash, A. | Journal Article | 2023 | Mapping endemic freshwater fish richness to identify high priority areas for conservation: an ecoregion approach |
| Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Najafi Chaloshtory, S., Yasser, A.G., Naser, M.D., Normandeau, E., Mashtizadeh, A., Elmi, A., Sedighi, O., Changizi, A., Hallerman, E. and Bernatchez, L. | Journal Article | 2023 | Flexibility of life to survive limitations: oral disc forms in the Tashan Cave barb Garra tashanensis |
| Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., Abdolahi‑Mousavi, S.E., Birgani, A.A., Normandeau, E., Hallerman, E., Bernatchez, L. and Freyhof, J. | Journal Article | 2024 | Distribution and conservation of subterranean fishes of Iran: insights from a new locality |
| Freyhof, J., Yoğurtçuoğlu, B., Jouladeh-Roudbar, A. and Kaya, C. | Book | 2025 | Handbook of freshwater Fishes of west Asia |
