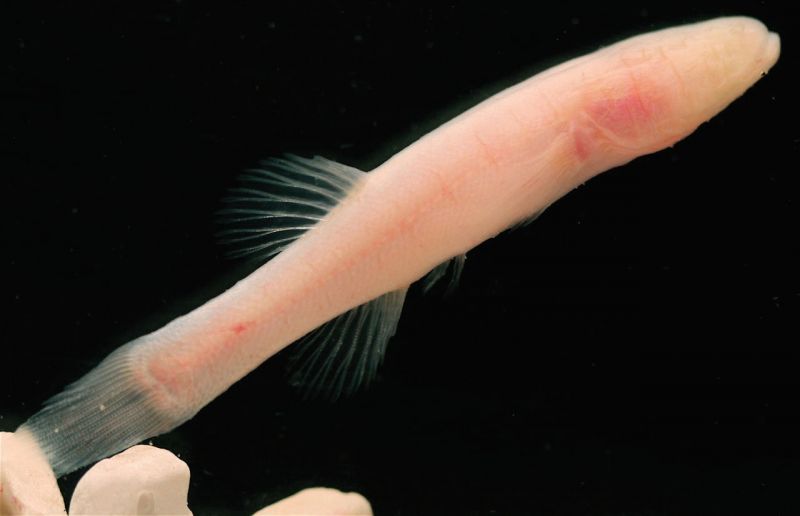
Amblyopsis hoosieri
Niemiller, Prejean and Chakrabarty 2014 in Chakrabarty, Prejean and Niemiller 2014
| ORDER | SUB-ORDER | FAMILY |
|---|---|---|
| Percopsiformes | Percopsiformes | Amblyopsidae |
Synonyms
Typhlichthys wyandotte Eigenmann 1905
Amblyopsis spelaea “N” Niemiller et al. 2013
Amblyopsis spelaea Woods and Inger 1957 (in part)
The common name is Hoosier Cavefish (Page et al. 2013, Adams et al. 2020)
Country
USATypes
Holotype: INHS 106675 75.1mm SL. Paratypes: INHS 40424 (12), INHS 60574 (1), INHS 102504 (4), LSUMZ 17419 (1), LSUMZ 17420 (1), UMMZ 90379 (2), UMMZ 113550 (1), UMMZ 114890 (2), UMMZ 144604 (1), UMMZ 146992 (1), UMMZ 146994 (3), UMMZ 157174 (1), UMMZ 157175 (1), UMMZ 160944 (1), YPM 25304 (2), YPM 25305 (1).
zoobank.org/688BC3D5-7773-41E8-961F-67E3E4902BE2
Distribution
Indiana, USA
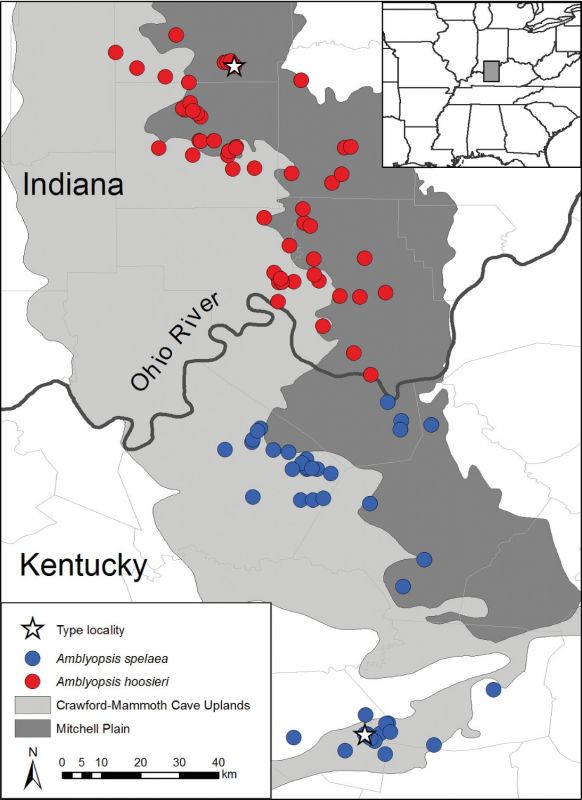
Type locailty: Bronson’s Cave (White River Dr.) Spring Mill State Park, Lawrence County, Indiana, USA, 38°44'N, 86°25'W. Also recorded from: Twin Caves, near Mitchell, Lawrence County; Sibert’s Well Cave, beside Wyandotte Cave; Lost River, ca. 2 mi NE of Orangeville; Donaldson’s Cave, Spring Mills State Park, Lawrence County; Stream in Sibert’s Well Cave, Wyandotte, Crawford County; Stream in Sheep Cave, near Wyandotte, Crawford County; Stream in Bronson Cave, Spring Mill State Park, Lawrence County; “possibly” Donaldson farm caves near Indiana University; Twin Cave, Mitchell, Lawrence County; Donaldson Cave, Spring Mill State Park, Lawrence County; Blue Springs Caverns, Lawrence County.
Keith (1988, 1989) surveyed caves and springs in Indiana. He found populations in 45 sites in Indiana. Eleven of the 45 sites in Indiana recorded by Keith were springs (i.e. resurgences) which suggests that this species may exist also in the phreatic zone. Welch and Keith (1974) surveyed caves in the Hoosier natinal Fprest. A study of the ecology of Amblyopsis hoosieri (as A. spelaea) in Blue Spring Cave, Indiana was conducted by Welch (1972). [Romero ansd Bennis (1998) noted that "this species is known from about 1800 caves in Indiana”. This figure is clearly in error].
Habitat
Inhabits cool (8-17oC) hypogean streams which have mixed mud/rock substrates in shoals, and mixed sand/silt substrates in pools (Burr and Warren 1986:219). Eleven of the 45 sites in Indiana recorded by Keith (1988, 1989) were springs (i.e. resurgences) which suggests that this species may exist also in the phreatic zone. A study of the ecology of A. hoosieri (as A. spelaea) in Blue Spring Cave, Indiana was conducted by Welch (1972).
Systematics
Until recently all populations of the Northern Cavefish, distributed in southern Indiana and Northern Kentucky, were considered to be Amblyopsis spelaea. However, genetic, morphological and geographical evidence show that the populations north (Indiana) and south (Kentucky) of the Ohio River are two separate species with Amblyopsis spelaea confined to Kentucky and with Amblyopsis hoosieri confined to Indiana (Chakrabarty et al. 2014).
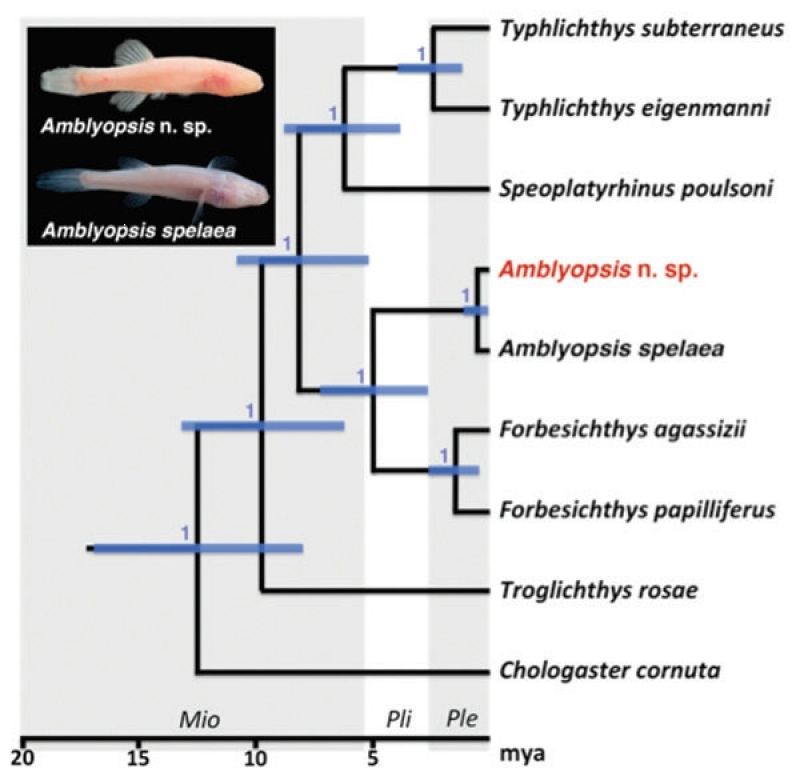
There are nine known and named taxa in the Family Amblyopsidae. Of these six are subterranean fishes with the usual troglomorphic characters of reduced eyes and pigment and permanent subterranean existence, and three are epigean fishes with normal eyes and pigment. Recent molecular and morphological evidence produced by Hart et al. (2020) demonstrates that the relationship between these hypogean and epigean fishes is not simple. There are four major clades within the Family:
1. Typhlichthys subterraneus and Typhlichthys eigenmanni are sister species and sister to this pair is Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni. However, T. subterraneus is quite clearly divided into two subgroups, one of which is closer to T. eigenmanni than it is to the other group of T. subterraneus. The only way to read the cladogram for this group is that it consists of three taxa, one of which is currently un-named. This clade are all subterranean fishes.
2. Two of the epigean fishes, Forbesichthys papilliferus and Forbesichthys agassizii, are sister to each other and their sister is the hypogean species Amblyopsis spelaea.
The two remaining clades contain one species each but their relationships to the other six species is ambiguous:
3a. Sister to the above groups is epigean Chologaster cornuta with hypogean Troglichthys rosae sister to all other taxa.
3b. Sister to the above groups is hypogean Troglichthys rosae with epigean Chologaster cornuta sister to all other taxa.
Given the fact that the distribution of Chologaster cornuta is very far from the distributions of the other taxa 3b seems the most parsimonious explanation. Amblyopsis hoosieri is not included in the paper of Hart et al. (in press) but one would expect it to be in group 2 above based on geography.
This analysis does not take into account the ten possible cryptic taxa, currently subsumed within Typhlichthys subterraneus, identified by Graening, Fenolio and Slay (2011), Niemiller et al. (2013) and Hart, Burress and Armbruster (2016).
Conservation Status
MuG [NE]
Museum Holdings
Because Amblyopsis hoosieri was, for most of the time since 1842, thought to be Amblyopsis spelaea it is likely that there are numerous specimens in various museums in the USA that are actually Amblyopsis hoosieri.
Key References
- Packard, A. S. and Putnam, F. W. (1872)
- Packard, A. S. (1888)
- Packard, A.S. (1894)
- Eigenmann, C.H. (1909)
- Poulson, T.L. (1961)
- Clay, W.M. (1962)
- Poulson, T.L. (1963)
- Poulson, T.L. (1964)
- Mohr, C.E. and Poulson, T.L. (1966)
- Welch, N. M. (1972)
- Welch, N.M. and Keith, J.H. (1974)
- Clay, W.M. (1975)
- Kalayil, P.K. and Clay, W.M. (1976)
- Keith, J.H. (1977)
- Keith, J.H. and Gray, L.M. (1979)
- Keith, J.H. and Poulson, T.L. (1981)
- Keith, J.H. and Powell, R.L. (1981)
- Keith, J.H. (1988)
- Keith, J.H. (1989)
- Keith, J.H. (1992)
- Keith, J.H., Bassett, J.L. and Duwelius, J.A. (1996)
- Poulson, T.L. (1997)
- Poulson, T.L. (1998)
- Niemiller, M.L. and Poulson, T.L. (2010)
- Niemiller, M. L., Near, T. J. and Fitzpatrick, B. M. (2011)
- Niemiller, M.L. (2011)
- Niemiller, M.L., Higgs, D.M. and Soares, D. (2013)
- Niemiller, M.L., McCandless, J.R., Reynolds, R.G., Caddle, J., Near, T.J., Tillquist, C.R., Pearson, W.D. and Fitzpatrick, B.M. (2013)
- Soares, D. Niemiller, M.L. and Higgs, D. (2014)
- Chakrabarty, P., Prejean, J.A. and Niemiller, M.L. (2014)
- Soares, D., Niemiller, M.L. and Higgs, D.M. (2016)
- Armbruster, J., Niemiller, M.L. and Hart, P.B. (2016)
- Helf, K. and Olson, R.A. (2017)
- Niemiller, M.L., Taylor, S.J., Slay, M.E. and Hobbs, H.H. III (2019)
- Mouser, J. (2019)
- Soares, D., and Niemiller, M.L. (2019)
- Adams, G.L., Burr, B.M. and Warren, M.L. (2020)
- Soares, D., and Niemiller, M.L. (2020)
- Groves, C., White, W. ,White, B., Palmer, A. and Palmer, P. (2020)
- Helf, K., Olson, R. and Toomey, R. (2020)
- White, W.B. (2020)
- Williams, J., Groves, C. and Bledsoe, L.A. (2020)
- Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. (2021)
- Bledsoe, L.A., Groves, C. and Toomey, R. (2021)
- Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. (2022)
- Mouser, J. (2022)
- McAllister, C.T., Fenolio, D.B., Slay, M.E., and Cloutman, D.G. (2023)
- Earl, D.J., Branch, E.C., Cole-Wick, A.A., Lee, Y., Rowe, L.M., Badra, P.J., Wilton, C.M., Cuthrell, D.L. and Sexton, N.H. (2024)
- Brownstein, C.D., Policarpo, M., Harrington, R.C., Hoffman, E.A., Stokes, M.F., Casane, D. and Near, T.J. (2025)
- Burgess, J., Gage, L., Brite, K., Leeper, R. and Buckmaster, S. (2025)
- Hoosier cavefish (2025)
- Niemiller, M.L., Hart, P.B., Pirro, S. and Arcila, D. (2025)
| Packard, A. S. and Putnam, F. W. | Book | 1872 | The Mammoth Cave and its inhabitants, a description of the fishes, insects and crustaceans found in the caves, etc |
| Packard, A. S. | Book | 1888 | The cave fauna of North America, with remarks on the anatomy of the brain and origin of the blind species |
| Packard, A.S. | Journal Article | 1894 | On the origin of the subterranean fauna of North America |
| Eigenmann, C.H. | Book | 1909 | Cave vertebrates of America, a study in degenerative evolution |
| Poulson, T.L. | Thesis | 1961 | Cave adaptation in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Clay, W.M. | Book | 1962 | A field manual of Kentucky fishes |
| Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1963 | Cave adaptation in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1964 | Life history and the control of population size in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Mohr, C.E. and Poulson, T.L. | Book | 1966 | The life of the cave |
| Welch, N. M. | Thesis | 1972 | Movement and ecology of the blind cave fish Amblyopsis spelaea |
| Welch, N.M. and Keith, J.H. | Journal Article | 1974 | Report on the occurence of the blindfish Amblyopsis spelaea DeKay in selected caves of the Hoosier National Forest |
| Clay, W.M. | Book | 1975 | The fishes of Kentucky |
| Kalayil, P.K. and Clay, W.M. | Journal Article | 1976 | Immumological characteristics and relationships of tissue antigens in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Keith, J.H. | Journal Article | 1977 | The "broken back syndrome" |
| Keith, J.H. and Gray, L.M. | Journal Article | 1979 | A preliminary study of the occurence of broken-back syndrome in the northern cave-fish (Amblyopsis spelaea) at Spring Mill State Park, Mitchell, Indiana |
| Keith, J.H. and Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1981 | Broken-back syndrome in Amblyopsis spelaea, Donaldson-Twin Cave, Indiana |
| Keith, J.H. and Powell, R.L. | Journal Article | 1981 | Evaluation of Mayfields Cave, Monroe County, Indiana, for eligability as a National landmark |
| Keith, J.H. | Journal Article | 1988 | Distribution of Northern Cavefish, Amblyopsis spelaea DeKay, in Indiana and Kentucky and reccommendations for its protection |
| Keith, J.H. | Journal Article | 1989 | A report on a field survey to determine the status of the Northern Cavefish (Amblyopsis spelaea DeKay) in Indiana |
| Keith, J.H. | Report | 1992 | A report on the possible impacts of State Road 37 construction activities on cave fauna and karst features |
| Keith, J.H., Bassett, J.L. and Duwelius, J.A. | Book Section | 1996 | INDOT implementation of a memorandum of understanding to reduce the impacts of highway construction in Indiana karst |
| Poulson, T.L. | Book Section | 1997 | Biodiversity in the Mammoth Cave region |
| Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1998 | Biology of cave fishes: A retrospective and prospective with emphasis on the Amblyopdidae |
| Niemiller, M.L. and Poulson, T.L. | Book Section | 2010 | Subterranean fishes of North America: Amblyopsidae |
| Niemiller, M. L., Near, T. J. and Fitzpatrick, B. M. | Journal Article | 2011 | Delimiting species using multilocus data: Diagnosing cryptic diversity in the Southern Cavefish, Typhlichthys Subterraneus (Teleostei: Amblyopsidae) |
| Niemiller, M.L. | Thesis | 2011 | Evolution, speciation, and conservation of amblyopsid cavefishes |
| Niemiller, M.L., Higgs, D.M. and Soares, D. | Journal Article | 2013 | Evidence for hearing loss in amblyopsid cavefishes |
| Niemiller, M.L., McCandless, J.R., Reynolds, R.G., Caddle, J., Near, T.J., Tillquist, C.R., Pearson, W.D. and Fitzpatrick, B.M. | Journal Article | 2013 | Effects of climatic and geological processes during the pleistocene on the evolutionary history of the Northern cavefish, Amblyopsis spelaea (Teleostei: Amblyopsidae) |
| Soares, D. Niemiller, M.L. and Higgs, D. | Journal Article | 2014 | Review article. Hearing and acoustic communication in cavefishes |
| Chakrabarty, P., Prejean, J.A. and Niemiller, M.L. | Journal Article | 2014 | The Hoosier cavefish, a new and endangered species (Amblyopsidae, Amblyopsis) from the caves of southern Indiana |
| Soares, D., Niemiller, M.L. and Higgs, D.M. | Journal Article | 2016 | Hearing in Cavefishes |
| Armbruster, J., Niemiller, M.L. and Hart, P.B. | Journal Article | 2016 | Morphological evolution of the cave-, spring-, and swampfishes of the Amblyopsidae |
| Helf, K. and Olson, R.A. | Book Section | 2017 | Subsurface aquatic ecology of Mammoth Cave |
| Niemiller, M.L., Taylor, S.J., Slay, M.E. and Hobbs, H.H. III | Book Section | 2019 | Biodiversity in the United States and Canada |
| Mouser, J. | Thesis | 2019 | Examining occurrence, life history, and ecology of cavefishes and cave crayfishes using both traditional and novel approaches |
| Soares, D., and Niemiller, M.L. | Journal Article | 2019 | Variation in cephalic neuromasts surface and cave-dwelling fishes of the family Amblyopsidae (Teleostei: Percopsiformes) |
| Adams, G.L., Burr, B.M. and Warren, M.L. | Book Section | 2020 | Amblyopsidae: Cavefishes |
| Soares, D., and Niemiller, M.L. | Journal Article | 2020 | Variation in cephalic neuromasts surface and cave-dwelling fishes of the family Amblyopsidae (Teleostei: Percopsiformes) |
| Groves, C., White, W. ,White, B., Palmer, A. and Palmer, P. | Web Page | 2020 | Karst hydrogeology of Mammoth Cave National Park: Why is the world’s longest known cave here? |
| Helf, K., Olson, R. and Toomey, R. | Web Page | 2020 | Mammoth Cave Ecology |
| White, W.B. | Web Page | 2020 | A blueprint for the assessment of inorganic carbon flow paths in the Great Onyx groundwater basin, Mammoth Cave National Park |
| Williams, J., Groves, C. and Bledsoe, L.A. | Web Page | 2020 | In-cave tracing to measure discharge in the Great Onyx flow system, Mammoth Cave National Park, Kentucky |
| Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. | Journal Article | 2021 | Refining sampling protocols for cavefishes and cave crayfishes to account for environmental variation |
| Bledsoe, L.A., Groves, C. and Toomey, R. | Journal Article | 2021 | The Mammoth Cave National Park world heritage site |
| Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. | Journal Article | 2022 | Lithology and disturbance drive cavefish and cave crayfish occurrence in the Ozark Highlands ecoregion |
| Mouser, J. | Journal Article | 2022 | Lithology and disturbance drive cavefish and cave crayfish occurrence in the Ozark Highlands ecoregion |
| McAllister, C.T., Fenolio, D.B., Slay, M.E., and Cloutman, D.G. | Journal Article | 2023 | First parasites (Cnidaria: Myxobolidae; Trematoda:Digenea: Clinostomidae) reported from the threatened Ozark Cavefish, Troglichthys rosae (Percopsiformes:Amblyopsidae), from Arkansas, U.S.A., with a summary of the parasites of North American cavefishes |
| Earl, D.J., Branch, E.C., Cole-Wick, A.A., Lee, Y., Rowe, L.M., Badra, P.J., Wilton, C.M., Cuthrell, D.L. and Sexton, N.H. | Report | 2024 | Assessing climate vulnerability and adaptive capacity of Midwest species of greatest conservation need |
| Brownstein, C.D., Policarpo, M., Harrington, R.C., Hoffman, E.A., Stokes, M.F., Casane, D. and Near, T.J. | Journal Article | 2025 | Convergent evolution in Amblyopsid cavefishes and the age of eastern North American subterranean ecosystems |
| Burgess, J., Gage, L., Brite, K., Leeper, R. and Buckmaster, S. | Journal Article | 2025 | Preliminary observations of terrestrial, aquatic, and aerial fauna in Breathing Hole Cave |
| Hoosier cavefish | Web Page | 2025 | Hoosier cavefish (Amblyopsis hoosieri) |
| Niemiller, M.L., Hart, P.B., Pirro, S. and Arcila, D. | Journal Article | 2025 | The complete genome sequences of 12 species of Percopsiformes |