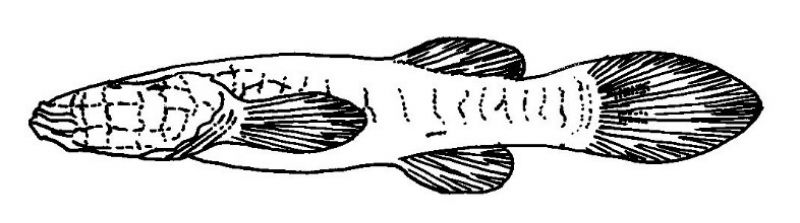
Troglichthys rosae
Eigenmann 1898
| ORDER | SUB-ORDER | FAMILY |
|---|---|---|
| Percopsiformes | Percopsiformes | Amblyopsidae |
Synonyms
Typhlichthys rosae Eigenmann 1898
Amblyopsis rosae (Eigenmann, 1898) Woods and Inger 1957
Amblyopsis rosae whitae Romero 1998 nomen nudum
Amblyopsis rosae arkansasus Romero 1998 nomen nudum
The common name is Ozark Cavefish (Page et al. 2013, Adams et al. 2020)
Country
USATypes
The accounts of Eigenmann (1898, 1899) make no mention of individual specimens, nor do they mention the number of animals available to him. The description is thus based on an unknown number of syntypes whose location is not known. The most important definition of the species is given by Woods and Inger (1957:245).
Distribution
Arkansas, Missouri and Oklahoma, USA.
Type locality: Sarcoxie, Jasper County, Missouri, USA (37o05’N, 94o10’W) (?, see note below). Willis and Brown (1985) made a thorough search of known locations and found the species in only 13 caves of 180 examined. United States Fish and Wildlie Service (1989, 1996) records that this species is “presently” known from 21 caves. The distribution is limited to the Springfield Plateau of the Ozark Highlands Province in northwest Arkansas, northeast Oklahoma and southwest Missouri. This species is nowhere sympatric with Typhlichthys subterraneus as was previously thought (Jones and Taber 1985).
Mouser et al. (2023) record this specie from 83 locations within the Ozark Highlands ecoregion.
(Note: Willis and Brown (1985:311) state that this species "was first collected in Sarcoxie Cave, Jasper County, Missouri by Garman (1889)" and in their reference list give page 232 of this source. In fact no mention is made anywhere in Garman (1889) of this cave. Woods and Inger (1957:245) give the type locality as "Sarcoxie, Missouri" and in their list of the range say "Jasper County: caves in or near Sarcoxie (Days Cave, Downers Cave.....)". Willis and Brown (1985:315, Table 1) synonymise Days Cave and Downers Cave with Sarcoxie Cave. Whether the type locality really is "Sarcoxie Cave" or whether it is Days Cave or Downers Cave, or indeed some other cave "in or near Sarcoxie" is not known to me.)
Habitat
This species is usually found in small cave streams where there is an upwelling of groundwater from the underlying aquifer.
Systematics
A DNA study by Bergstrom, Noltie and Holtsford (1995, 1997, 1998) and Bergstrom (1997) suggests that all of the populations studied cluster together and that they lie some distance from any other populations of amblyopsids. These preliminary data indicate that rosae is a monophyletic clade with some considerable divergence within it.
Mouser et al. (2023) recorded this species from a new location: "Troglichthys (= Amblyopsis) rosae (Ozark Cavefish) is currently known from 83 locations within the Ozark Highlands ecoregion. We found a cavefish at a new location in the Grand Lake O’ the Cherokees on the western side of the Neosho River (Delaware County, OK), which is on the northwest periphery of the Ozark Cavefish range. Examination of the mitochondrial ND2 gene supports that the specimen is an Ozark Cavefish, but distinct (4.6–9.2% pairwise distance) from other specimens that have been genetically sampled, and could represent a unique population. Future research should focus on expanding sampling efforts and conducting a range-wide genetic analysis of the Ozark Cavefish" (from their Abstract).
There are nine known and named taxa in the Family Amblyopsidae. Of these six are subterranean fishes with the usual troglomorphic characters of reduced eyes and pigment and permanent subterranean existence, and three are epigean fishes with normal eyes and pigment. Recent molecular and morphological evidence produced by Hart et al. (2020) demonstrates that the relationship between these hypogean and epigean fishes is not simple. There are four major clades within the Family:
1. Typhlichthys subterraneus and Typhlichthys eigenmanni are sister species and sister to this pair is Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni. However, T. subterraneus is quite clearly divided into two subgroups, one of which is closer to T. eigenmanni than it is to the other group of T. subterraneus. The only way to read the cladogram for this group is that it consists of three taxa, one of which is currently un-named. This clade are all subterranean fishes.
2. Two of the epigean fishes, Forbesichthys papilliferus and Forbesichthys agassizii, are sister to each other and their sister is the hypogean species Amblyopsis spelaea.
The two remaining clades contain one species each but their relationships to the other six species is ambiguous:
3a. Sister to the above groups is epigean Chologaster cornuta with hypogean Troglichthys rosae sister to all other taxa.
3b. Sister to the above groups is hypogean Troglichthys rosae with epigean Chologaster cornuta sister to all other taxa.
Given the fact that the distribution of Chologaster cornuta is very far from the distributions of the other taxa 3b seems the most parsimonious explanation. Amblyopsis hoosieri is not included in the paper of Hart et al. (in press) but one would expect it to be in group 2 above based on geography.
This analysis does not take into account the ten possible cryptic taxa, currently subsumed within Typhlichthys subterraneus, identified by Graening, Fenolio and Slay (2011), Niemiller et al. (2013) and Hart, Burress and Armbruster (2016).
Conservation Status
(NatureServe. 2014. Amblyopsis rosae. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014: http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-3.RLTS.T1079A19032420.en. Downloaded on 10 July 2017).
V (Miller 1977), Seriously threatened (Willis and Brown 1985:316), Threatened (Williams, Johnson, Hendrickson, Contreras-Balderas, Williams., Navarro-Mendoza, McAllister and Deacon 1989),V (IUCN1988, 1990, 1993), Threatened (United States Fish and Wildlife Service 1989 1994a,b), VU D1+2 (IUCN 1996, 2000), G2/G3 (NatureServe 2002).
Museum Holdings
KU 3210, 14007, 14169; OSUMZ 7105, 7106, 7271, 7848 (Tafanelli and Russell, 1972; Mayden and Cross, 1983; Moore, 1972); Also specimens at FMNH, MU, UMMZ, and USNM (Woods and Inger, 1957:245); BMNH.
Key References
- Cox, U.O. (1905)
- Eigenmann, C.H. (1909)
- Woods, L.P. and Inger, R.F. (1957)
- Poulson, T.L. (1961)
- Rosen, D.E. (1962)
- Poulson, T.L. (1963)
- Poulson, T.L. (1969)
- Moore, G. (1972)
- Tafanelli, R. and Russell, J. E. (1972)
- Kalayil, P.K. and Clay, W.M. (1976)
- Swofford, D.L. (1976)
- Cooper, J. E. (1980)
- Swofford, D.L., Branson, B.A. and Sievert, G.A. (1980)
- Bechler, D.L. (1980)
- Bechler, D.L. (1981)
- Bechler, D.L. (1981)
- Brown, A.V., Brown, K.B., Willis, L.D., Jackson, D.C. and Brussock, P.P. (1982)
- Bechler, D.L. (1983)
- Mayden, R. L. and Cross, F. B. (1983)
- Willis, L. D. (1984)
- Brown, A. V. and Willis, L. D. (1984)
- Poulson, T.L. (1985)
- Willis, L.D. and Brown, A.V. (1985)
- Brown, A. V. and Todd, C. S. (1987)
- Brown, A.V., Graening, G.O. and Vendrell, P. (1988)
- Palunas, M.J. (1989)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1989)
- Willis, L.D. and Stewart, J.H. (1989)
- Means, M.L. (1993)
- Means, M. and Johnson, J.E. (1995)
- Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. (1995)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1996)
- Brown, J.Z. (1996)
- Canaday, B. D. and Vitello, C. B. (1996)
- Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. (1997)
- Brown, J.Z., Boyd, G.L. and Johnson, J.E. (1997)
- Boyd, G.L. (1997)
- Elliott, W.R. (1998)
- Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. (1998)
- Romero, A. (1998)
- Graening, G.O. (1998)
- Graening, G.O. (2000)
- Graening, G.O. and Brown, A.V. (2000)
- Brown, J. Z. and Johnson, J. E. (2001)
- Poulson, T. (2001)
- Noltie, D. B. and Wicks, C.M. (2001)
- Adams, G.L. and Johnson, J.E. (2001)
- Aley, T., Ashley, D.C., Elliott, W.R., McGlimsey, M., Weaver, D. and Beard, J. (2002)
- Elliott, W.R. (2003)
- Poly, WJ and Wetzel, JE (2003)
- Graening, G.O. and Brown, A.V. (2003)
- Poly, W.J. and Proudlove, G.S. (2004)
- Graening, G.O. (2005)
- Graening, G.O. and Fenolio, D.B. (2005)
- Elliott, W.R. (2007)
- Aley, T., Aley, C., Moss, P. and Hertzler, T. (2008)
- Graening, G.O., Fenolio, D.B., Niemiller, M.L., Brown, A.V. and Beard, J.B. (2010)
- Niemiller, M. L., Near, T. J. and Fitzpatrick, B. M. (2011)
- Niemiller, M.L. (2011)
- Graening, G.O., Fenolio, D.B. and Slay, M.E. (2011)
- Mouser, J. (2019)
- Niemiller, M.L., Taylor, S.J., Slay, M.E. and Hobbs, H.H. III (2019)
- Adams, G.L., Burr, B.M. and Warren, M.L. (2020)
- Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. (2021)
- Mouser, J. (2022)
- Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. (2022)
- Mouser, J.B., Johnston, J., Niemiller, M.L., and Brewer, S.K. (2023)
- McAllister, C.T., Fenolio, D.B., Slay, M.E., and Cloutman, D.G. (2023)
- Ugarte, E. (2025)
- Niemiller, M.L., Hart, P.B., Pirro, S. and Arcila, D. (2025)
- Brownstein, C.D., Policarpo, M., Harrington, R.C., Hoffman, E.A., Stokes, M.F., Casane, D. and Near, T.J. (2025)
| Cox, U.O. | Journal Article | 1905 | A revision of the cave fishes of North America |
| Eigenmann, C.H. | Book | 1909 | Cave vertebrates of America, a study in degenerative evolution |
| Woods, L.P. and Inger, R.F. | Journal Article | 1957 | The cave, spring and swamp fishes of the family Amblyopsidae of central and eastern United States |
| Poulson, T.L. | Thesis | 1961 | Cave adaptation in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Rosen, D.E. | Journal Article | 1962 | Comments on the relationships of the North American cave fishes of the family Amblyopsidae |
| Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1963 | Cave adaptation in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1969 | Population size, density and regulation in cave fishes |
| Moore, G. | Journal Article | 1972 | [Untitled note relating to the Whitewater Creek flood control dam record of Amblyopsis rosae] |
| Tafanelli, R. and Russell, J. E. | Journal Article | 1972 | An extension of the range of the blind cave fish Amblyopsis rosae |
| Kalayil, P.K. and Clay, W.M. | Journal Article | 1976 | Immumological characteristics and relationships of tissue antigens in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Swofford, D.L. | Thesis | 1976 | Genetic variability, population differentiation and biochemical relationships in the family Amblyopsidae |
| Cooper, J. E. | Book Section | 1980 | Amblyopsis rosae (Eigenmann), Ozark cavefish |
| Swofford, D.L., Branson, B.A. and Sievert, G.A. | Journal Article | 1980 | Genetic differentiation of cavefish populations (Amblyopsidae) |
| Bechler, D.L. | Thesis | 1980 | The evolution of agonistic behaviour in amblyopsid fishes |
| Bechler, D.L. | Journal Article | 1981 | Behavioral studies on the Amblyopsidae; the cave, spring and swamp fish |
| Bechler, D.L. | Journal Article | 1981 | Agonistic behaviour in the Amblyopsidae; the cave, spring and swamp fishes |
| Brown, A.V., Brown, K.B., Willis, L.D., Jackson, D.C. and Brussock, P.P. | Journal Article | 1982 | Distribution and abundance of the Ozark cave fish Amblyopsis rosae (Eigenmann), in Missouri |
| Bechler, D.L. | Journal Article | 1983 | The evolution of agonistic behaviour in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Mayden, R. L. and Cross, F. B. | Journal Article | 1983 | Reevaluation of the Oklahoma records of the southern cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus (Amblyopsidae) |
| Willis, L. D. | Thesis | 1984 | Distribution and habitat requirements of the Ozark cavefish, Amblyopsis rosae |
| Brown, A. V. and Willis, L. D. | Journal Article | 1984 | Cavefish (Amblyopsis rosae) in Arkansas: Populations, incidence, habitat requirements and mortality factors |
| Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1985 | Evolutionary reduction by neutral mutations: Plausibility arguments and data from Amblyopsid fishes and Linyphiid spiders |
| Willis, L.D. and Brown, A.V. | Journal Article | 1985 | Distribution and habitat requirements of the Ozark cavefish, Amblyopsis rosae |
| Brown, A. V. and Todd, C. S. | Journal Article | 1987 | Status review of the threated Ozark cavefish Amblyosis rosae |
| Brown, A.V., Graening, G.O. and Vendrell, P. | Report | 1988 | Monitoring cavefish populations and environmental quality in Cave Springs Cave, Arkansas |
| Palunas, M.J. | Journal Article | 1989 | Life histories of the Amblyopsidae with an emphasis on reproductive cycles |
| U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | Book | 1989 | Ozark cavefish recovery plan |
| Willis, L.D. and Stewart, J.H. | Report | 1989 | A recovery plan for Ozark cavefish (Amblyopsis rosae) |
| Means, M.L. | Thesis | 1993 | Population dynamics and movement of Ozark cavefish in Logan Cave NWR, Benton County, Arkansas, with additional baseline water quality information |
| Means, M. and Johnson, J.E. | Journal Article | 1995 | Movement of threatened Ozark cavefish in Logan Cave national wildlife refuge, Arkansas |
| Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. | Journal Article | 1995 | Ozark cavefish genetics: The phylogeny of Missouri's Ozark cavefish (Amblyopsis rosae) and southern cavefish (Typhlichthys subterraneus) |
| U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | Journal Article | 1996 | Amblyopsis rosae |
| Brown, J.Z. | Thesis | 1996 | Population dynamics and movement of Ozark cavefish in Logan Cave national wildlife refuge, Benton County, Arkansas |
| Canaday, B. D. and Vitello, C. B. | Journal Article | 1996 | Ozark cavefish public outreach and habitat management project |
| Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. | Book Section | 1997 | Molecular phylogenetics and historical biogeography of the family Amblyopsidae |
| Brown, J.Z., Boyd, G.L. and Johnson, J.E. | Book Section | 1997 | Ozark cavefish in Logan Cave National Wildlife Refuge: A five year perspective |
| Boyd, G.L. | Thesis | 1997 | Metabolic rates and life history of aquatic organisms inhabiting Logan Cave stream in northwest Arkansas |
| Elliott, W.R. | Book Section | 1998 | Conservation of the North American cave and karst biota |
| Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. | Journal Article | 1998 | The phylogeny, historical biogeography, and evolution of troglobitism in Amblyopsis rosae (Ozark cavefish) and Typhlichthys subterraneus (southern cavefish) |
| Romero, A. | Journal Article | 1998 | Threatened fishes of the world: Amblyopsis rosae (Eigenmann, 1898) (Amblyopsidae) |
| Graening, G.O. | Journal Article | 1998 | Biospeleology as the basis of groundwater management |
| Graening, G.O. | Journal Article | 2000 | Ecosystem dynamics of an Ozark cave |
| Graening, G.O. and Brown, A.V. | Report | 2000 | Trophic dynamics and pollution effects in Cave Springs Cave, Arkansas. |
| Brown, J. Z. and Johnson, J. E. | Journal Article | 2001 | Population biology and growth of Ozark cavefishes in Logan Cave National Wildlife refuge, Arkansas |
| Poulson, T. | Journal Article | 2001 | Morphological and physiological correlates of evolutionary reduction of metabolic rate among amblyopsid cave fishes |
| Noltie, D. B. and Wicks, C.M. | Journal Article | 2001 | How hydrogeology has shaped the ecology of Missouri's Ozark cavefish, Amblyopsis rosae, and southern cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus: Insights on the sightless from understanding the underground |
| Adams, G.L. and Johnson, J.E. | Journal Article | 2001 | Metabolic rate and natural history of Ozark cavefish, Amblyopsis rosae, in Logan Cave, Arkansas |
| Aley, T., Ashley, D.C., Elliott, W.R., McGlimsey, M., Weaver, D. and Beard, J. | Book | 2002 | Conserving Missouri's caves and karst |
| Elliott, W.R. | Book | 2003 | A guide to Missouri's cave life |
| Poly, WJ and Wetzel, JE | Journal Article | 2003 | Transbrachioral spawning: novel reproductive strategy observed for the pirate perch Aphredodereus sayanus (Aphredoderidae) |
| Graening, G.O. and Brown, A.V. | Journal Article | 2003 | Ecosystem dynamics and pollution effects in an Ozark cave stream |
| Poly, W.J. and Proudlove, G.S. | Journal Article | 2004 | Family Amblyopsdae Bonaparte 1846 |
| Graening, G.O. | Journal Article | 2005 | Trophic structure of Ozark cave streams containing endangered species |
| Graening, G.O. and Fenolio, D.B. | Journal Article | 2005 | Status update of the Delaware County cave crayfish, Cambarus subterraneus (Decapoda: Cambaridae) |
| Elliott, W.R. | Journal Article | 2007 | Zoogeography and biodiversity of Missouri cave and karst |
| Aley, T., Aley, C., Moss, P. and Hertzler, T. | Journal Article | 2008 | Hydrogeological characteristics of delineated recharge areas for 40 biologically significant cave and spring systems in Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma and Illinois |
| Graening, G.O., Fenolio, D.B., Niemiller, M.L., Brown, A.V. and Beard, J.B. | Journal Article | 2010 | The 30-year recovery effort for the Ozark cavefish (Amblyopsis rosae): analysis of current distribution, population trends, and conservation status of this threatened species |
| Niemiller, M. L., Near, T. J. and Fitzpatrick, B. M. | Journal Article | 2011 | Delimiting species using multilocus data: Diagnosing cryptic diversity in the Southern Cavefish, Typhlichthys Subterraneus (Teleostei: Amblyopsidae) |
| Niemiller, M.L. | Thesis | 2011 | Evolution, speciation, and conservation of amblyopsid cavefishes |
| Graening, G.O., Fenolio, D.B. and Slay, M.E. | Book | 2011 | Cave life of Oklahoma and Arkansas: exploration and conservation of subterranean biodiversity |
| Mouser, J. | Thesis | 2019 | Examining occurrence, life history, and ecology of cavefishes and cave crayfishes using both traditional and novel approaches |
| Niemiller, M.L., Taylor, S.J., Slay, M.E. and Hobbs, H.H. III | Book Section | 2019 | Biodiversity in the United States and Canada |
| Adams, G.L., Burr, B.M. and Warren, M.L. | Book Section | 2020 | Amblyopsidae: Cavefishes |
| Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. | Journal Article | 2021 | Refining sampling protocols for cavefishes and cave crayfishes to account for environmental variation |
| Mouser, J. | Journal Article | 2022 | Lithology and disturbance drive cavefish and cave crayfish occurrence in the Ozark Highlands ecoregion |
| Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. | Journal Article | 2022 | Lithology and disturbance drive cavefish and cave crayfish occurrence in the Ozark Highlands ecoregion |
| Mouser, J.B., Johnston, J., Niemiller, M.L., and Brewer, S.K. | Journal Article | 2023 | A Fisherman's Tale: An unusual observation of the Ozark Cavefish, Troglichthys (= Amblyopsis) rosae (Eigenmann) |
| McAllister, C.T., Fenolio, D.B., Slay, M.E., and Cloutman, D.G. | Journal Article | 2023 | First parasites (Cnidaria: Myxobolidae; Trematoda:Digenea: Clinostomidae) reported from the threatened Ozark Cavefish, Troglichthys rosae (Percopsiformes:Amblyopsidae), from Arkansas, U.S.A., with a summary of the parasites of North American cavefishes |
| Ugarte, E. | Thesis | 2025 | Urbanization, climate change, and water quality in northwest Arkansas caves |
| Niemiller, M.L., Hart, P.B., Pirro, S. and Arcila, D. | Journal Article | 2025 | The complete genome sequences of 12 species of Percopsiformes |
| Brownstein, C.D., Policarpo, M., Harrington, R.C., Hoffman, E.A., Stokes, M.F., Casane, D. and Near, T.J. | Journal Article | 2025 | Convergent evolution in Amblyopsid cavefishes and the age of eastern North American subterranean ecosystems |