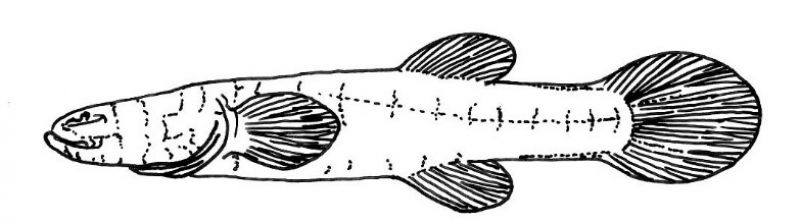
Typhlichthys subterraneus
Girard 1859
| ORDER | SUB-ORDER | FAMILY |
|---|---|---|
| Percopsiformes | Percopsiformes | Amblyopsidae |
Synonyms
Typhlichthys osborni Eigenmann 1905
Typhlichthys wyandotte Eigenmann 1905
Typhlichthys eigenmanni Hubbs 1938 (nomen nudum)
The common name is Southern Cavefish (Page et al. 2013, Adams et al. 2020)
Country
USATypes
Description based on a syntype series of three individuals: USNM 8563. This species is the type species by monotypy of the cave restricted genus Typhlichthys.
Distribution
Alabama, Georgi, Kentucky, Tennessee, posssibly Arkansas, USA
Type locality: a well near Bowling Green, Kentucky, USA (37o00’N, 86o30’W), the exact location of the well is not known. The range is discontinuous, with a western component including central and southern Missouri, and northern Arkansas, and an eastern component which extends from the south‑central tip of Indiana, southwards through Kentucky, into central Tennessee, northern Alabama and the north west tip of Georgia (35-40oN, 85-95oW). The Mississippi River runs between these two areas and other major rivers divide the range. Although once thought to be resident in Oklahoma this species is in fact absent from this state. Mayden and Cross (1983) have shown that all records of T. subterraneus from Oklahoma are in fact of Troglichthys rosae. Records from Greene County, Missouri have been shown by Jones and Taber (1985) to be in error and therefore the indication in Woods and Inger (1957:245) that T. subterraneus and T. rosae are sympatric no longer holds. These two species do not overlap in distribution. In Mammoth cave, Kentucky, but nowhere else, this species coexists with A. spelaea and Woods and Inger (1957) have suggested that this is because of competitive exclusion. This range lies within an area bounded by the southernmost limit of glaciation and the northernmost limit of the Cretaceous Mississippi embayment. In Mammoth Cave, Kentucky this species coexists with Amblyopsis spelaea and in Key Cave, Alabama with Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni.
Niemiller et al. (2016) report a significant range extension for the species to Catoosa Co. Georgia.
Habitat
Inhabits cool (10‑14oC) lentic waters over substata of mixed gravel, sand, and mud (Burr and Warren 1986:221). The preferred habitat of this species is in shallow streams fed by vertical shaft drains and with a moderate food supply (Poulson 1961, 1963 and pers. comm.). Schubert (1993), Schubert, Nielsen and Noltie (1993) and Schubert and Noltie (1995) made an experimental study of the substrate preference of this species. In all tests it significantly preferred cobbles to any other substrate. Cobbles have interstices large enough for the fishes to hide in and they spent much time there. Schubert and Noltie (1996) studied feeding. Compson (2004) used an isotopic study to show that T. subterraneaus, and probably also Amblyopsis spelaea, is a top predator within the cave ecosystem (see also Helf and Olson 2017). This species was known from Hidden River Cave but was extirpated from it, along with all other naturally occuring fauna, by intense pollution by sewage. After this problem was dealt with the natural fauna slowly recolonised the cave and T. subterraneus reappeared in 1993 and was still present in 2014 (Lewis et al. 1982, Lewis 1995, Jones and Pearson 1997, Lewis et al. 2015, Helf and Olson 2017 section 14.4.1, Table 14.3).
Systematics
Until the revision of Woods and Inger (1957) there were three nominal species of Typhlichthys, a fourth nominal species was based on a nomen nudum and was therefore invalid (Poly and Proudlove 2004). The population from Sloans Valley Cave, Pulaski County, Kentucky differs in a number of ways from other populations and may represent an undescribed taxon (Cooper and Beiter 1972, Burr and Warren 1986:221). No further details of this population have been published. Genetically, however, the populations are very distinct, even those that are close geographically (Swofford, Branson, and Sievert 1980). This genetic information supports the hypothesis of Cooper and Iles (1971) that morphological similarity may be more a matter of similar selective regimes resulting in parallel evolution than any significant gene flow which is difficult to support because of the major river divides to the range. Barr and Holsinger (1985) support this idea and suggest that the “species” is a composed of several local phylogenetic species separated by extrinsic dispersal barriers (i.e. rivers and non‑karstic geology). Swofford, Branson and Sievert (1980) however suggest that morphological and genetic divergence have been uncoupled. See below for more recent data.
Rosen (1962) has suggested that all Amblyopsid fishes be placed in a separate order, the Amblyopsiformes. This suggestion has not been followed by subsequent authors (e.g. Greenwood, Rosen, Weitzman and Myers 1966, Nelson, Grande and Wison 2016).
There are nine known and named taxa in the Family Amblyopsidae. Of these six are subterranean fishes with the usual troglomorphic characters of reduced eyes and pigment and permanent subterranean existence, and three are epigean fishes with normal eyes and pigment. Recent molecular and morphological evidence produced by Hart et al. (2020) demonstrates that the relationship between these hypogean and epigean fishes is not simple. There are four major clades within the Family:
1. Typhlichthys subterraneus and Typhlichthys eigenmanni are sister species and sister to this pair is Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni. However, T. subterraneus is quite clearly divided into two subgroups, one of which is closer to T. eigenmanni than it is to the other group of T. subterraneus. The only way to read the cladogram for this group is that it consists of three taxa, one of which is currently un-named. This clade are all subterranean fishes.
2. Two of the epigean fishes, Forbesichthys papilliferus and Forbesichthys agassizii, are sister to each other and their sister is the hypogean species Amblyopsis spelaea.
The two remaining clades contain one species each but their relationships to the other six species is ambiguous:
3a. Sister to the above groups is epigean Chologaster cornuta with hypogean Troglichthys rosae sister to all other taxa.
3b. Sister to the above groups is hypogean Troglichthys rosae with epigean Chologaster cornuta sister to all other taxa.
Given the fact that the distribution of Chologaster cornuta is very far from the distributions of the other taxa 3b seems the most parsimonious explanation. Amblyopsis hoosieri is not included in the paper of Hart et al. (in press) but one would expect it to be in group 2 above based on geography.
This analysis does not take into account the ten possible cryptic taxa, currently subsumed within Typhlichthys subterraneus, identified by Graening, Fenolio and Slay (2011), Niemiller et al. (2013) and Hart, Burress and Armbruster (2016).
Conservation Status
MuG [NT:3.1:2014] NT:3.1:2013 (Niemiller et al. 2013)
(NatureServe. 2014. Typhlichthys subterraneus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014: http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-3.RLTS.T22599A18236225.en. Downloaded on 10 July 2017).
Threatened (Branson 1981), Special concern (Burr and Warren 1986:221), VU D2 (IUCN 1996, 2000), G4 (NatureServe 2001).
Museum Holdings
KU 12853, SIUC 4129, 4130, 4131 (Mayden and Cross 1983); UMMZ 136379 (4 specimens) (Jones and Taber 1985); UAIC 656, AU 2067 (Cooper and Iles1971); UMMZ 133844 (formerly catalogued asTroglichthys rosae), ASUMZ 9064 (Paige, Tumlinson, and Mc Daniel 1981); also specimens at USNM, CAS‑SU, FMHM, MU, KU (Woods and Inger 1957); BMNH. KU:KUIT:8754, UAIC 14148.01 (Malmstrom et al. 2017, used for genome sequencing).
Probably many other specimens in museums in the USA.
ANSP, AUM, CAS, CMN, FMNH, KU, MCZ, MOSU, SIUC, TU, UAIC, UF, UL, UMMZ, USNM, UTIC, YPM (Niemiller et al. 2013)
Internet Resources
Genome https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/69345
Key References
- Davidson, R. (1840)
- Thompson, W. (1844)
- Girard, C. (1859)
- Packard, A. S. and Putnam, F. W. (1872)
- Packard, A. S. (1888)
- Packard, A.S. (1894)
- Cox, U.O. (1905)
- Eigenmann, C.H. (1909)
- Verrier, M. L. (1929)
- Bailey, V. (1933)
- Bailey, V (1933)
- Woods, L.P. and Inger, R.F. (1957)
- Poulson, T.L. (1961)
- Clay, W.M. (1962)
- Rosen, D.E. (1962)
- Poulson, T.L. (1963)
- Cooper, J.E. (1966)
- Branson, B.A. (1967)
- Barr, T.C. (1967)
- Poulson, T.L. (1968)
- Poulson, T.L. (1969)
- Cooper, J. E. (1969)
- Barr, T.C. and Kuehne, R.A. (1971)
- Cooper, J. E. and Cooper, M. R. (1971)
- Cooper, J. E. and Iles, A. (1971)
- Cooper, J. E. (1971)
- Cooper, J. E. and Beiter, D. P. (1972)
- Cooper, J.E. (1974)
- Cooper, J.E. (1975)
- Clay, W.M. (1975)
- Bechler, D.L. (1976)
- Kalayil, P.K. and Clay, W.M. (1976)
- Swofford, D.L. (1976)
- McNulty, J. A. (1978)
- Bechler, D.L. (1980)
- Duchon, K. and Lisowski, E.A. (1980)
- Cooper, J.E. (1980)
- Swofford, D.L., Branson, B.A. and Sievert, G.A. (1980)
- Smith, V. J. (1980)
- Paige, K. N., Tumlinson, C. R. and McDaniel, V. R. (1981)
- Bechler, D.L. (1981)
- Branson, B.A. (1981)
- Bechler, D.L. (1981)
- Vandike, J.E. (1981)
- Lisowski, E.A. and Poulson, T.L. (1981)
- Lewis, J.J., Lewis, T.M. and Eckstein, J. (1982)
- Swofford, D.L. (1982)
- Bechler, D.L. (1983)
- Mayden, R. L. and Cross, F. B. (1983)
- Lisowski, E. A. (1983)
- Vandike, J.E. (1984)
- Poulson, T.L. (1985)
- Crunkilton, R. (1985)
- Jones, S.R. and Taber, C.A. (1985)
- Burr, B.M. and Warren, M.L. (1986)
- Lewis, J.J. (1988)
- Hobbs, H.H. III and Bagley, F.M. (1989)
- Palunas, M.J. (1989)
- Branson, B.A. (1991)
- Poulson, T.L. (1992)
- Poulson, T.L. (1992)
- Rheams, K.F., Moser, P.H. and McGregor, S.W. (1992)
- Moser, P.H. and Rheams, K.F. (1992)
- Wilson, M. and Robison, A. (1993)
- Schubert, A.L.S., Nielsen, C.D. and Noltie, D.B. (1993)
- McGregor, S.W., Rheams, K.F., O’Neil, P.E., Moser, P.H. and Blackwood, R. (1994)
- Lewis, J.J. (1995)
- Pearson, W.D. and Boston, C.H. (1995)
- Schubert, A. L. S. and Noltie, D. B. (1995)
- Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. (1995)
- Schubert, A. L. S. and Noltie, D. B. (1996)
- Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. (1997)
- Green, S.M. and Romero, A. (1997)
- McGregor, S.W., Rheams, K.F., O’Neil, P.E., Moser, P.H. and Blackwood, R. (1997)
- Jones, T.G. and Pearson, W.D. (1997)
- Campbell, C.W., Sullivan, S.M. and Livingston, L.R. (1997)
- Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. (1998)
- Romero, A. (1998)
- Romero, A. (1998)
- Romero, A. (1998)
- Romero, A. and Bennis, L. (1998)
- Pearson, W.D. and Jones, T.G. (1998)
- Elliott, W.R. (1998)
- Culver, D.C. (1999)
- Noltie, D. B. and Wicks, C.M. (2001)
- Poulson, T. (2001)
- Lewis, J.J. (2002)
- Aley, T., Ashley, D.C., Elliott, W.R., McGlimsey, M., Weaver, D. and Beard, J. (2002)
- Poly, WJ and Wetzel, JE (2003)
- Aumiller, S.R. and Noltie, D.B. (2003)
- Elliott, W.R. (2003)
- Poly, W.J. and Proudlove, G.S. (2004)
- Compson, Z.G. (2004)
- Ruhl, M (2005)
- Romero, A. and Woodward, J.S. (2005)
- Romero, A. and Conner, M. (2007)
- Elliott, W.R. (2007)
- Aley, T., Aley, C., Moss, P. and Hertzler, T. (2008)
- Niemiller, ML and Fitzpatrick, BM (2008)
- Romero, A., Connor, M.S. and Vaughan, G.L. (2010)
- Cooper, J.E. and Cooper, M.R. (2011)
- Niemiller, M. L., Near, T. J. and Fitzpatrick, B. M. (2011)
- Niemiller, M.L. (2011)
- Niemiller, M.L. and Fitzpatrick, B.M. (2012)
- Niemiller, M.L., McCandless, J.R., Reynolds, R.G., Caddle, J., Near, T.J., Tillquist, C.R., Pearson, W.D. and Fitzpatrick, B.M. (2012)
- Miller, C. (2013)
- Niemiller, M.L. and Zigler, K.S. (2013)
- Niemiller, M.L., Fitzpatrick, B.M., Shah, P., Schmitz, L. and Near, T.J. (2013)
- Niemiller, M.L., Graening, G.O., Fenolio, D.B., Godwin, J.C., Cooley, J.R., Pearson, W.D., Fitzpatrick, B.M. and Near, T.J. (2013)
- Niemiller, M.L. and Fitzpatrick, B.M. (2013)
- Niemiller, M.L., Higgs, D.M. and Soares, D. (2013)
- Venarsky, M.P., Huntsman, B.M., Huryn, A.D., Benstead, J.P. and Kuhajda, B.R. (2014)
- Soares, D. Niemiller, M.L. and Higgs, D. (2014)
- Lewis, J.J., Lewis, S. and Nims, P. (2015)
- Armbruster, J., Niemiller, M.L. and Hart, P.B. (2016)
- Niemiller, M.L., Zigler, K.S., Hart, P.B., Kuhajda, B.R., Armbruster, J., Ayala, B.N. and Engel, A.S. (2016)
- Hart, PB (2016)
- Niemiller, M.L., Zigler, K.S., Stephen, C.D.R., Carter, E.T., Paterson, A.T., Taylor, S.J. and Engel, A.S. (2016)
- Soares, D., Niemiller, M.L. and Higgs, D.M. (2016)
- Malmstrøm, M., Matschiner, M., Tørresen, O.K., Jakobsen K.S. and Jentoft, S. (2017)
- Burress, P.B.H., Burress, E.D. and Armbruster, J. (2017)
- Toomey, R.., Hobbs, H.H. and Olson, R.A. (2017)
- White, W.B. and White, E.L. (2017)
- Poulson, T.L. (2017)
- Helf, K. and Olson, R.A. (2017)
- Culver, D.C. and Hobbs, H.H. (2017)
- Hobbs, H.H., Olson, R., Winkler, E.G. and Culver, D.C. (2017)
- O’Dell, G.A. and George, A.I. (2018)
- Ponta, G.M.L., McGregor, S.W. and Jones, S.W. (2018)
- Niemiller, M.L., Taylor, S.J., Slay, M.E. and Hobbs, H.H. III (2019)
- Trimboli, S.R. and Toomey, R.S. (2019)
- Mouser, J. (2019)
- Soares, D., and Niemiller, M.L. (2020)
- Groves, C., White, W. ,White, B., Palmer, A. and Palmer, P. (2020)
- Helf, K., Olson, R. and Toomey, R. (2020)
- White, W.B. (2020)
- Ponta, G.M.L., McGregor, S.W. and Blackwood, R. (2020)
- Ponta, G. (2020)
- Williams, J., Groves, C. and Bledsoe, L.A. (2020)
- Adams, G.L., Burr, B.M. and Warren, M.L. (2020)
- Zigler, K.S., Niemiller, M.L., Stephen, C.D.R., Ayala, B.N. Milne, M.A., Gladstone, N.S., Engel, A.S., Jensen, J.B., Camp, C.D., Ozier, J.C. and Cressler, A. (2020)
- Hart, P.B., Niemiller, M.L., Burress, E.D., Armbruster, J.W., Ludt, W.B. and Chakrabarty, P. (2020)
- Holler Jr., C., Mays, J.D., and Niemiller, M.L (2020)
- Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. (2021)
- Niemiller, M.L., Helf, K. and Toomey, R.S. (2021)
- Bledsoe, L.A., Groves, C. and Toomey, R. (2021)
- Mouser, J. (2022)
- Dooley, K.E., Niemiller, K.D.K., Sturm, N. and Niemiller, M.L. (2022)
- Flack, A. (2022)
- Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. (2022)
- Niemiller, M.L., Slay, M.E., Inebnit, T., Miller, B., Tobin, B., Cramphorn, B., Hinkle, A., Jones, B.D., Mann, N., Niemiller, K.D.K. and Pitts, S. (2023)
- Niemiller, M.L., Zigler, K.S., Hinkle, A., Stephen, C.D.R., Cramphorn, B., Higgs, J. Mann, N., Miller, B.T., Niemiller, K.D.K., Smallwood, K. and Hardy, J. (2023)
- McAllister, C.T., Fenolio, D.B., Slay, M.E., and Cloutman, D.G. (2023)
- Cecil, M. (2023)
- Hart, P.B., Niemiller, M.L., Armbruster, J.W. and Chakrabarty, P. (2023)
- Niemiller, M.L., Hart, P.B., Pirro, S. and Arcila, D. (2025)
- Brownstein, C.D., Policarpo, M., Harrington, R.C., Hoffman, E.A., Stokes, M.F., Casane, D. and Near, T.J. (2025)
| Davidson, R. | Book | 1840 | An excursion to the Mammoth Cave and the Barrens of Kentucky,with some notices of the early settlement of the state |
| Thompson, W. | Journal Article | 1844 | Notice of the blind-fish, crayfish and insects from the Mammoth Cave, Kentucky |
| Girard, C. | Journal Article | 1859 | Ichthyological notices |
| Packard, A. S. and Putnam, F. W. | Book | 1872 | The Mammoth Cave and its inhabitants, a description of the fishes, insects and crustaceans found in the caves, etc |
| Packard, A. S. | Book | 1888 | The cave fauna of North America, with remarks on the anatomy of the brain and origin of the blind species |
| Packard, A.S. | Journal Article | 1894 | On the origin of the subterranean fauna of North America |
| Cox, U.O. | Journal Article | 1905 | A revision of the cave fishes of North America |
| Eigenmann, C.H. | Book | 1909 | Cave vertebrates of America, a study in degenerative evolution |
| Verrier, M. L. | Journal Article | 1929 | Observations sur le comportement d'un poisson cavernicole: Typhlichthys osbornii Eigenmann |
| Bailey, V. | Journal Article | 1933 | Fishes of the caves and cave region |
| Bailey, V | Journal Article | 1933 | Cave life of Kentucky: Mainly in the Mammoth Cave region |
| Woods, L.P. and Inger, R.F. | Journal Article | 1957 | The cave, spring and swamp fishes of the family Amblyopsidae of central and eastern United States |
| Poulson, T.L. | Thesis | 1961 | Cave adaptation in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Clay, W.M. | Book | 1962 | A field manual of Kentucky fishes |
| Rosen, D.E. | Journal Article | 1962 | Comments on the relationships of the North American cave fishes of the family Amblyopsidae |
| Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1963 | Cave adaptation in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Cooper, J.E. | Journal Article | 1966 | Preliminary observations on the biology of Shelta Cave, Alabama |
| Branson, B.A. | Journal Article | 1967 | [Not known] |
| Barr, T.C. | Journal Article | 1967 | Ecological studies in the Mammoth Cave System of Kentucky. I.The biota |
| Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1968 | Aquatic cave communities |
| Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1969 | Population size, density and regulation in cave fishes |
| Cooper, J. E. | Journal Article | 1969 | Biological studies in Shelta Cave, Alabama |
| Barr, T.C. and Kuehne, R.A. | Journal Article | 1971 | Ecological studies in the Mammoth Cave System of Kentucky. II. The Ecosystem |
| Cooper, J. E. and Cooper, M. R. | Journal Article | 1971 | Studies on the aquatic ecology of Shelta Cave, Huntsville, Alabama |
| Cooper, J. E. and Iles, A. | Journal Article | 1971 | The Southern Cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus, at the southeastern periphery of its range |
| Cooper, J. E. | Journal Article | 1971 | Interesting new locality records for the southern cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus Girard (Pisces, Amblyopsidae) |
| Cooper, J. E. and Beiter, D. P. | Journal Article | 1972 | The Southern Cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus (Pisces, Amblyopsidae), in the eastern Mississippian Plateau of kentuck |
| Cooper, J.E. | Journal Article | 1974 | New distributional and ecological data for Typhlichthys subterraneus (Pisces, Amblyopsidae) and subterranean Gyrinophilus (Amphibia, Plethodontidae) |
| Cooper, J.E. | Thesis | 1975 | Ecological and behavioural studies in Shelta Cave, Alabama, with emphasis on decapod crustaceans |
| Clay, W.M. | Book | 1975 | The fishes of Kentucky |
| Bechler, D.L. | Journal Article | 1976 | Typhlichthys subterraneus Girard (Pisces, Amblyopsidae) in the Jackson Plain of Tennessee |
| Kalayil, P.K. and Clay, W.M. | Journal Article | 1976 | Immumological characteristics and relationships of tissue antigens in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Swofford, D.L. | Thesis | 1976 | Genetic variability, population differentiation and biochemical relationships in the family Amblyopsidae |
| McNulty, J. A. | Journal Article | 1978 | Fine ultrastucture of the pineal organ of the troglodytic fish Typhlichyes subterraneous |
| Bechler, D.L. | Thesis | 1980 | The evolution of agonistic behaviour in amblyopsid fishes |
| Duchon, K. and Lisowski, E.A. | Journal Article | 1980 | Draft environmental assessment of Lock and Dam Six, Green River Navigation Project, on Mammoth Cave National Park |
| Cooper, J.E. | Book Section | 1980 | Typhlichthys subterraneus Girard Southern cavefish |
| Swofford, D.L., Branson, B.A. and Sievert, G.A. | Journal Article | 1980 | Genetic differentiation of cavefish populations (Amblyopsidae) |
| Smith, V. J. | Thesis | 1980 | Some aspects of the life history of the southern cavefish (Typhlichthys subterraneus Girard) in Missouri |
| Paige, K. N., Tumlinson, C. R. and McDaniel, V. R. | Journal Article | 1981 | A second record of Typhlichthys subterraneus (Pisces, Amblyopsidae) from Arkansas, USA |
| Bechler, D.L. | Journal Article | 1981 | Behavioral studies on the Amblyopsidae; the cave, spring and swamp fish |
| Branson, B.A. | Journal Article | 1981 | Endangered, threatened and rare animals and plants of Kentucky |
| Bechler, D.L. | Journal Article | 1981 | Agonistic behaviour in the Amblyopsidae; the cave, spring and swamp fishes |
| Vandike, J.E. | Journal Article | 1981 | The effects of the November 1981 liquid fertiliser pipeline break on groundwater in Phelps County, Missouri |
| Lisowski, E.A. and Poulson, T.L. | Book Section | 1981 | Impacts of Lock and Dam Six on base level ecosystems in Mammoth Cave |
| Lewis, J.J., Lewis, T.M. and Eckstein, J. | Book Section | 1982 | A biological reconnaissance of a poluted cave stream: the Hidden River grounwater basin |
| Swofford, D.L. | Thesis | 1982 | Genetic variability, population differentiation and biochemical relationships in the family Amblyopsidae |
| Bechler, D.L. | Journal Article | 1983 | The evolution of agonistic behaviour in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Mayden, R. L. and Cross, F. B. | Journal Article | 1983 | Reevaluation of the Oklahoma records of the southern cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus (Amblyopsidae) |
| Lisowski, E. A. | Journal Article | 1983 | Distribution, habitat and behaviour of the Kentucky cave shrimp Palaemonias ganteri Hay |
| Vandike, J.E. | Book Section | 1984 | Hydrogeologic aspects of the November 1981 liquid fertiliser pipeline break on groundwater in the Meramec Spring recharge area, Phelps County, Missouri |
| Poulson, T.L. | Journal Article | 1985 | Evolutionary reduction by neutral mutations: Plausibility arguments and data from Amblyopsid fishes and Linyphiid spiders |
| Crunkilton, R. | Book Section | 1985 | Subterranean contamination of Meramec Spring by ammonium nitrate and urea fertiliser and its implications for rare cave biota |
| Jones, S.R. and Taber, C.A. | Journal Article | 1985 | A range revision for western populations of the southern cavefish Typhlichthys subterraneus (Amblyopsidae) |
| Burr, B.M. and Warren, M.L. | Journal Article | 1986 | A distributional atlas of Kentucky fishes |
| Lewis, J.J. | Thesis | 1988 | The systematics, zoogeography and life history of the troglobitic Isopods of the Interior Plateaus of the eastern United States |
| Hobbs, H.H. III and Bagley, F.M. | Book | 1989 | Shelta Cave management plan |
| Palunas, M.J. | Journal Article | 1989 | Life histories of the Amblyopsidae with an emphasis on reproductive cycles |
| Branson, B.A. | Journal Article | 1991 | The Mammoth Cave blindfish |
| Poulson, T.L. | Book Section | 1992 | The Mammoth Cave ecosystem |
| Poulson, T.L. | Book Section | 1992 | Case studies of groundwater biomonitoring in the Mammoth Cave region |
| Rheams, K.F., Moser, P.H. and McGregor, S.W. | Report | 1992 | Geologic, hydrologic and biologic investigations in Arrowwood, Bobcat, Matthews and Shelta caves and selected caves, Madison County, Alabama |
| Moser, P.H. and Rheams, K.F. | Report | 1992 | Hydrogeologic investigations of Shelta and Bobcat Caves and adjoining areas, Madison County, Alabama |
| Wilson, M. and Robison, A. | Report | 1993 | Contaminant concentrations in water and sediments from Shelta Cave |
| Schubert, A.L.S., Nielsen, C.D. and Noltie, D.B. | Journal Article | 1993 | Habitat use and gas bubble disease in southern cavefish (Typhlichthys subterraneus) |
| McGregor, S.W., Rheams, K.F., O’Neil, P.E., Moser, P.H. and Blackwood, R. | Report | 1994 | Biological, geological and hydrological investigations in Bobcat, Matthews, and Shelta caves and other selected caves in north Alabama |
| Lewis, J.J. | Book Section | 1995 | The devastation and recovery of caves and karst affected by industrialisation |
| Pearson, W.D. and Boston, C.H. | Report | 1995 | Distribution and status of the Northern Cavefish, Amblyopsis spelaea: Final report to the Indiana Department of Natural Resources Division of Fish and Wildlife Program |
| Schubert, A. L. S. and Noltie, D. B. | Journal Article | 1995 | Laboratory studies of substrate and microhabitat selection in southern cavefish (Typhlichthys subterraneus Girard) |
| Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. | Journal Article | 1995 | Ozark cavefish genetics: The phylogeny of Missouri's Ozark cavefish (Amblyopsis rosae) and southern cavefish (Typhlichthys subterraneus) |
| Schubert, A. L. S. and Noltie, D. B. | Journal Article | 1996 | Effects if feeding regime on prey consumption and weight change rate in captive southern cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus Girard (Pisces: Percopsiformes: Amblyopsidae) |
| Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. | Book Section | 1997 | Molecular phylogenetics and historical biogeography of the family Amblyopsidae |
| Green, S.M. and Romero, A. | Journal Article | 1997 | Responses to light in two blind cave fishes (Amblyopsis spelaea and Typhlichthys subterraneus) (Pisces: Amblyopsidae) |
| McGregor, S.W., Rheams, K.F., O’Neil, P.E., Moser, P.H. and Blackwood, R. | Journal Article | 1997 | Biological, geological and hydrological investigations in Bobcat, Matthews, and Shelta caves and other selected caves in north Alabama |
| Jones, T.G. and Pearson, W.D. | Conference Paper | 1997 | The recovery of the aquatic biological community in Hidden River Cave, Horse Cave, Kentucky |
| Campbell, C.W., Sullivan, S.M. and Livingston, L.R. | Book Section | 1997 | Modeling of a cave ecosystem |
| Bergstrom, D.E., Noltie, D.B. and Holtsford, T.P. | Journal Article | 1998 | The phylogeny, historical biogeography, and evolution of troglobitism in Amblyopsis rosae (Ozark cavefish) and Typhlichthys subterraneus (southern cavefish) |
| Romero, A. | Journal Article | 1998 | Threatened fishes of the world: Typhlichthys subterraneus Girard, 1860 (Amblyopsidae) |
| Romero, A. | Journal Article | 1998 | Threatened fishes of the world: Amblyopsis rosae (Eigenmann, 1898) (Amblyopsidae) |
| Romero, A. | Journal Article | 1998 | Threatened fishes of the world: Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni Cooper and Kuehne, 1974 (Amblyopsidae) |
| Romero, A. and Bennis, L. | Journal Article | 1998 | Threatened fishes of the world: Amblyopsis spelaea De Kay, 1842 (Amblyopsidae) |
| Pearson, W.D. and Jones, T.G. | Report | 1998 | Final Report based on a faunal inventory of subterranean streams and development of a cave aquatic biological monitoring program using a modified index of biotic integrity |
| Elliott, W.R. | Book Section | 1998 | Conservation of the North American cave and karst biota |
| Culver, D.C. | Conference Paper | 1999 | A history of management of biological resources of Shelta Cave, Alabama, USA |
| Noltie, D. B. and Wicks, C.M. | Journal Article | 2001 | How hydrogeology has shaped the ecology of Missouri's Ozark cavefish, Amblyopsis rosae, and southern cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus: Insights on the sightless from understanding the underground |
| Poulson, T. | Journal Article | 2001 | Morphological and physiological correlates of evolutionary reduction of metabolic rate among amblyopsid cave fishes |
| Lewis, J.J. | Report | 2002 | Conservation assessment for Southern cavefish (Typhlichthys subterraneus) |
| Aley, T., Ashley, D.C., Elliott, W.R., McGlimsey, M., Weaver, D. and Beard, J. | Book | 2002 | Conserving Missouri's caves and karst |
| Poly, WJ and Wetzel, JE | Journal Article | 2003 | Transbrachioral spawning: novel reproductive strategy observed for the pirate perch Aphredodereus sayanus (Aphredoderidae) |
| Aumiller, S.R. and Noltie, D.B. | Journal Article | 2003 | Chemoreceptive responses of the southern cavefish Typhlichthys subterraneus Girard, 1860 (Pisces, Amblyopsidae) to conspecifics and prey |
| Elliott, W.R. | Book | 2003 | A guide to Missouri's cave life |
| Poly, W.J. and Proudlove, G.S. | Journal Article | 2004 | Family Amblyopsdae Bonaparte 1846 |
| Compson, Z.G. | Thesis | 2004 | An isotopic examination of cave, spring and epigean trophic structures in Mammoth Cave National Park |
| Ruhl, M | Thesis | 2005 | Flow reversal events increase the abundance of nontroglomorphic fish in the subterranean rivers of Mammoth Cave National Park |
| Romero, A. and Woodward, J.S. | Journal Article | 2005 | On white fish and black men: Did Stephen Bishop really discover the blind cave fish of Mammoth Cave |
| Romero, A. and Conner, M. | Journal Article | 2007 | Status report for the southern cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus in Arkansas |
| Elliott, W.R. | Journal Article | 2007 | Zoogeography and biodiversity of Missouri cave and karst |
| Aley, T., Aley, C., Moss, P. and Hertzler, T. | Journal Article | 2008 | Hydrogeological characteristics of delineated recharge areas for 40 biologically significant cave and spring systems in Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma and Illinois |
| Niemiller, ML and Fitzpatrick, BM | Journal Article | 2008 | Phylogenetics of the Southern cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus: Implications for conservation and management |
| Romero, A., Connor, M.S. and Vaughan, G.L. | Journal Article | 2010 | Population Status of the Southern Cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus in Arkansas |
| Cooper, J.E. and Cooper, M.R. | Journal Article | 2011 | Observations on the biology of the endangered stygobitic shrimp Palaemonias alabamae, with notes on P. ganteri (Decapoda: Atyidae) |
| Niemiller, M. L., Near, T. J. and Fitzpatrick, B. M. | Journal Article | 2011 | Delimiting species using multilocus data: Diagnosing cryptic diversity in the Southern Cavefish, Typhlichthys Subterraneus (Teleostei: Amblyopsidae) |
| Niemiller, M.L. | Thesis | 2011 | Evolution, speciation, and conservation of amblyopsid cavefishes |
| Niemiller, M.L. and Fitzpatrick, B.M. | Journal Article | 2012 | Status and life history of the amblyopsid cavefishes in Kentucky |
| Niemiller, M.L., McCandless, J.R., Reynolds, R.G., Caddle, J., Near, T.J., Tillquist, C.R., Pearson, W.D. and Fitzpatrick, B.M. | Journal Article | 2012 | Effects of climatic and geological processes during the Pleistocene on the evolutionary history of the Northern Cavefish, Amblyopsis Spelaea (Teleostei: Amblyopsidae) |
| Miller, C. | Thesis | 2013 | Ecosystem disturbance and recovery in Shelta Cave |
| Niemiller, M.L. and Zigler, K.S. | Journal Article | 2013 | Patterns of cave biodiversity and endemism in the Appalachians and interior plateau of Tennessee |
| Niemiller, M.L., Fitzpatrick, B.M., Shah, P., Schmitz, L. and Near, T.J. | Journal Article | 2013 | Evidence for repeated loss of selective constraint in rhodopsin of amblyopsid cavefishes (Teleostei: Amblyopsidae) |
| Niemiller, M.L., Graening, G.O., Fenolio, D.B., Godwin, J.C., Cooley, J.R., Pearson, W.D., Fitzpatrick, B.M. and Near, T.J. | Journal Article | 2013 | Doomed before they are described? The need for conservation assessments of cryptic species complexes using an amblyopsid cavefish (Amblyopsidae: Typhlichthys) as a case study |
| Niemiller, M.L. and Fitzpatrick, B.M. | Report | 2013 | Status, life history, and phylogenetics of amblyopsid cavefishes in Kentucky |
| Niemiller, M.L., Higgs, D.M. and Soares, D. | Journal Article | 2013 | Evidence for hearing loss in amblyopsid cavefishes |
| Venarsky, M.P., Huntsman, B.M., Huryn, A.D., Benstead, J.P. and Kuhajda, B.R. | Journal Article | 2014 | Quantitative food web analysis supports the energy‑limitation hypothesis in cave stream ecosystems |
| Soares, D. Niemiller, M.L. and Higgs, D. | Journal Article | 2014 | Review article. Hearing and acoustic communication in cavefishes |
| Lewis, J.J., Lewis, S. and Nims, P. | Report | 2015 | Observations on the ecosystem of Hidden River Cave bioinventory: Community cencus and water quality analysis |
| Armbruster, J., Niemiller, M.L. and Hart, P.B. | Journal Article | 2016 | Morphological evolution of the cave-, spring-, and swampfishes of the Amblyopsidae |
| Niemiller, M.L., Zigler, K.S., Hart, P.B., Kuhajda, B.R., Armbruster, J., Ayala, B.N. and Engel, A.S. | Journal Article | 2016 | First definitive record of a stygobiotic fish (Percopsiformes, Amblyopsidae, Typhlichthys) from the Appalachians karst region in the eastern United States |
| Hart, PB | Thesis | 2016 | Diversity and conservation of the Southern Cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus |
| Niemiller, M.L., Zigler, K.S., Stephen, C.D.R., Carter, E.T., Paterson, A.T., Taylor, S.J. and Engel, A.S. | Journal Article | 2016 | Vertebrate fauna in caves of eastern tennessee within the Appalachians karst region, USA |
| Soares, D., Niemiller, M.L. and Higgs, D.M. | Journal Article | 2016 | Hearing in Cavefishes |
| Malmstrøm, M., Matschiner, M., Tørresen, O.K., Jakobsen K.S. and Jentoft, S. | Journal Article | 2017 | Whole genome sequencing data and de novo draft assemblies for 66 teleost species |
| Burress, P.B.H., Burress, E.D. and Armbruster, J. | Journal Article | 2017 | Body shape variation within the Southern Cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus (Percopsiformes: Amblyopsidae) |
| Toomey, R.., Hobbs, H.H. and Olson, R.A. | Book Section | 2017 | An orientation to Mammoth Cave and this volume |
| White, W.B. and White, E.L. | Book Section | 2017 | Hydrology and hydrogeology of Mammoth Cave |
| Poulson, T.L. | Book Section | 2017 | Terrestrial cave ecology of the Mammoth Cave region |
| Helf, K. and Olson, R.A. | Book Section | 2017 | Subsurface aquatic ecology of Mammoth Cave |
| Culver, D.C. and Hobbs, H.H. | Book Section | 2017 | Biodiversity of Mammoth Cave |
| Hobbs, H.H., Olson, R., Winkler, E.G. and Culver, D.C. | Book | 2017 | Mammoth Cave: A Human and Natural History |
| O’Dell, G.A. and George, A.I. | Journal Article | 2018 | The celebrated black explorer Stephen Bishop and Mammoth Cave: Observations by an English journalist in 1853 |
| Ponta, G.M.L., McGregor, S.W. and Jones, S.W. | Report | 2018 | Hydrogeological assessment of Key Cave, Lauderdale County, Alabama |
| Niemiller, M.L., Taylor, S.J., Slay, M.E. and Hobbs, H.H. III | Book Section | 2019 | Biodiversity in the United States and Canada |
| Trimboli, S.R. and Toomey, R.S. | Journal Article | 2019 | Temperature and reverse-flow patterns of the River Styx, Mammoth Cave, Kentucky |
| Mouser, J. | Thesis | 2019 | Examining occurrence, life history, and ecology of cavefishes and cave crayfishes using both traditional and novel approaches |
| Soares, D., and Niemiller, M.L. | Journal Article | 2020 | Variation in cephalic neuromasts surface and cave-dwelling fishes of the family Amblyopsidae (Teleostei: Percopsiformes) |
| Groves, C., White, W. ,White, B., Palmer, A. and Palmer, P. | Web Page | 2020 | Karst hydrogeology of Mammoth Cave National Park: Why is the world’s longest known cave here? |
| Helf, K., Olson, R. and Toomey, R. | Web Page | 2020 | Mammoth Cave Ecology |
| White, W.B. | Web Page | 2020 | A blueprint for the assessment of inorganic carbon flow paths in the Great Onyx groundwater basin, Mammoth Cave National Park |
| Ponta, G.M.L., McGregor, S.W. and Blackwood, R. | Conference Paper | 2020 | Time series hydrologic monitoring within karst aquifers of Key Cave and Cathedral Caverns, Alabama |
| Ponta, G. | Web Page | 2020 | Monitoring karst aquifers in north Alabama for the protection of sensitive aquatic biota |
| Williams, J., Groves, C. and Bledsoe, L.A. | Web Page | 2020 | In-cave tracing to measure discharge in the Great Onyx flow system, Mammoth Cave National Park, Kentucky |
| Adams, G.L., Burr, B.M. and Warren, M.L. | Book Section | 2020 | Amblyopsidae: Cavefishes |
| Zigler, K.S., Niemiller, M.L., Stephen, C.D.R., Ayala, B.N. Milne, M.A., Gladstone, N.S., Engel, A.S., Jensen, J.B., Camp, C.D., Ozier, J.C. and Cressler, A. | Journal Article | 2020 | Biodiversity from caves and other subterranean habitats of Georgia, USA |
| Hart, P.B., Niemiller, M.L., Burress, E.D., Armbruster, J.W., Ludt, W.B. and Chakrabarty, P. | Journal Article | 2020 | Cave-adapted evolution in the North American Amblyopsid fishes Inferred using phylogenomics and geometric morphometrics |
| Holler Jr., C., Mays, J.D., and Niemiller, M.L | Journal Article | 2020 | The fauna of caves and other subterranean habitats of North Carolina, USA |
| Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. | Journal Article | 2021 | Refining sampling protocols for cavefishes and cave crayfishes to account for environmental variation |
| Niemiller, M.L., Helf, K. and Toomey, R.S. | Journal Article | 2021 | Mammoth Cave: A hotspot of subterranean biodiversity in the United States |
| Bledsoe, L.A., Groves, C. and Toomey, R. | Journal Article | 2021 | The Mammoth Cave National Park world heritage site |
| Mouser, J. | Journal Article | 2022 | Lithology and disturbance drive cavefish and cave crayfish occurrence in the Ozark Highlands ecoregion |
| Dooley, K.E., Niemiller, K.D.K., Sturm, N. and Niemiller, M.L. | Journal Article | 2022 | Rediscovery and phylogenetic analysis of the Shelta Cave Crayfish (Orconectes sheltae Cooper and Cooper, 1997), a decapod (Decapoda, Cambaridae) endemic to Shelta Cave in northern Alabama, USA |
| Flack, A. | Journal Article | 2022 | Dark degenerations: Life, light, and transformation beneath the Earth, 1840–circa 1900 |
| Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. | Journal Article | 2022 | Lithology and disturbance drive cavefish and cave crayfish occurrence in the Ozark Highlands ecoregion |
| Niemiller, M.L., Slay, M.E., Inebnit, T., Miller, B., Tobin, B., Cramphorn, B., Hinkle, A., Jones, B.D., Mann, N., Niemiller, K.D.K. and Pitts, S. | Journal Article | 2023 | Fern Cave: A hotspot of subterranean biodiversity in the Interior Low Plateau karst region of Alabama in the southeastern United States |
| Niemiller, M.L., Zigler, K.S., Hinkle, A., Stephen, C.D.R., Cramphorn, B., Higgs, J. Mann, N., Miller, B.T., Niemiller, K.D.K., Smallwood, K. and Hardy, J. | Journal Article | 2023 | The Crystal-Wonder cave system: A new hotspot of subterranean biodiversity in the southern Cumberland Plateau of south-central Tennessee, USA |
| McAllister, C.T., Fenolio, D.B., Slay, M.E., and Cloutman, D.G. | Journal Article | 2023 | First parasites (Cnidaria: Myxobolidae; Trematoda:Digenea: Clinostomidae) reported from the threatened Ozark Cavefish, Troglichthys rosae (Percopsiformes:Amblyopsidae), from Arkansas, U.S.A., with a summary of the parasites of North American cavefishes |
| Cecil, M. | Thesis | 2023 | Hydrological dynamics of surface-groundwater interactions between major springs of Mammoth Cave and the Green River, Kentucky, USA |
| Hart, P.B., Niemiller, M.L., Armbruster, J.W. and Chakrabarty, P. | Journal Article | 2023 | Conservation implications for the world’s most widely distributed cavefish species complex based on population genomics (Typhlichthys, Percopsiformes) |
| Niemiller, M.L., Hart, P.B., Pirro, S. and Arcila, D. | Journal Article | 2025 | The complete genome sequences of 12 species of Percopsiformes |
| Brownstein, C.D., Policarpo, M., Harrington, R.C., Hoffman, E.A., Stokes, M.F., Casane, D. and Near, T.J. | Journal Article | 2025 | Convergent evolution in Amblyopsid cavefishes and the age of eastern North American subterranean ecosystems |