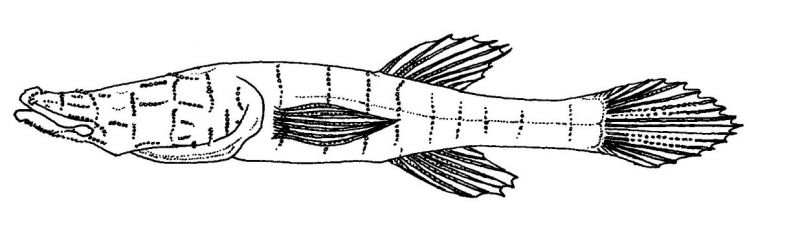
Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni
Cooper and Kuehne 1974
| ORDER | SUB-ORDER | FAMILY |
|---|---|---|
| Percopsiformes | Percopsiformes | Amblyopsidae |
Synonyms
None.
The common name is Alabama Cavefish (Page et al. 2013, Adams et al. 2020)
Country
USATypes
Holotype: USNM 204999 adult female (with ova) 58.3 mm SL. Paratypes ("paratopotypes" of Cooper and Kuehne 1974): USNM 204998 3 specimens; UMMZ 197679 2 specimens; ALA (UAIC in Cooper and Kuehne 1974) 3705 2 specimens, 31.2-48.4mm SL. One specimen reported to be in the collection of T.L. Poulson was never in fact received by him (T.L. Poulson pers. comm.) and the location of this specimen is not known. This is the type species by original designation and monotypy of the cave‑restricted genus Speoplatyrhinus.
Distribution
Alabama, USA.
Known only from the type locality: Key Cave, Lauderdale County, Alabama, USA (34o51’N, 87o40’W). Caves to the west of Key Cave, which may once have held populations, are now inundated after the creation of Pickwick Lake on the Tennessee River. Collier Cave (also known as Collier Slough Bone Cave) lies within the aquifer seen in Key Cave and may be potential site for this species though it has never been seen there. Bell Cave, Elbow Cave and Watkins Sink Cave are also candidates for additional populations (U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service 1985, 1990, Kuhajda and Mayden 2001). Typhlichthys subterraneus is also recorded from Key Cave (Steve Walsh pers. comm. and John Cooper pers. comm.).
Habitat
Key cave contains sections of deep clear water and several bat roosts. There is an abundant aquatic fauna of stygobitic crayfishes (Procambarus pecki and Cambarus jonesi), amphipods, and isopods and a dense terrestrial invertebrate fauna from the bat guano. The diet probably also includes copepods. Key Cave is an important site for the endangered Gray Bat, Myotis grisesens, and it is thought that the presence of the bats is of vital importance to the cave fishes as their guano will provide direct and indirect sources of food.
Systematics
This is the most troglomorphic of all amblyopsid fishes.
There are nine known and named taxa in the Family Amblyopsidae. Of these six are subterranean fishes with the usual troglomorphic characters of reduced eyes and pigment and permanent subterranean existence, and three are epigean fishes with normal eyes and pigment. Recent molecular and morphological evidence produced by Hart et al. (2020) demonstrates that the relationship between these hypogean and epigean fishes is not simple. There are four major clades within the Family:
1. Typhlichthys subterraneus and Typhlichthys eigenmanni are sister species and sister to this pair is Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni. However, T. subterraneus is quite clearly divided into two subgroups, one of which is closer to T. eigenmanni than it is to the other group of T. subterraneus. The only way to read the cladogram for this group is that it consists of three taxa, one of which is currently un-named. This clade are all subterranean fishes.
2. Two of the epigean fishes, Forbesichthys papilliferus and Forbesichthys agassizii, are sister to each other and their sister is the hypogean species Amblyopsis spelaea.
The two remaining clades contain one species each but their relationships to the other six species is ambiguous:
3a. Sister to the above groups is epigean Chologaster cornuta with hypogean Troglichthys rosae sister to all other taxa.
3b. Sister to the above groups is hypogean Troglichthys rosae with epigean Chologaster cornuta sister to all other taxa.
Given the fact that the distribution of Chologaster cornuta is very far from the distributions of the other taxa 3b seems the most parsimonious explanation. Amblyopsis hoosieri is not included in the paper of Hart et al. (in press) but one would expect it to be in group 2 above based on geography.
This analysis does not take into account the ten possible cryptic taxa, currently subsumed within Typhlichthys subterraneus, identified by Graening, Fenolio and Slay (2011), Niemiller et al. (2013) and Hart, Burress and Armbruster (2016).
Conservation Status
MG TLO [CR B1ab(iii)+2ab(iii):3.1:2013]
(NatureServe. 2013. Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2013: http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T20467A19033986.en. Downloaded on 10 July 2017). E (Miller 1977), E (U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service 1987), V (IUCN 1988), E (Williams, Johnson, Hendrickson, Balderas-Balderas, Williams., Navarro-Mendoza, McAllister and Deacon 1989), E (IUCN 1990, 1993), E (U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service 1994, 1994), CR C2b (IUCN 1996, 2000), G1 (NatureServe 2002). Key Cave is now located within the Key Cave National Wildlife Refuge. This is an area of protected land in the recharge area for Key Cave and it is hoped that deleterious actions and events will be avoided or reduced (United States Fish and Wildlife Service 1996).
Museum Holdings
As above only.
Internet Resources
Key References
- Cooper, J.E. (1968)
- Cooper, J.E. and Kuehne, R.A. (1974)
- Bechler, D.L. (1980)
- Cooper, J.E. (1980)
- Bechler, D.L. (1981)
- Bechler, D.L. (1981)
- US Fish and Wildlife Service (1982)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1982)
- Bechler, D.L. (1983)
- Cobb, R.M. (1985)
- Cobb, R.M. (1986)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1987)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1988)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1990)
- Aley, T. (1990)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1991)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1994)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1996)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1996)
- Romero, A. (1998)
- Kidd, R.E., Taylor, C.T. and Stricklin, V.E. (2001)
- Poulson, T. (2001)
- Kuhajda, B.R. and Mayden, R.L. (2001)
- Poly, WJ and Wetzel, JE (2003)
- Poly, W.J. and Proudlove, G.S. (2004)
- Kuhajda, B.R. (2004)
- Niemiller, ML and Fitzpatrick, BM (2008)
- Niemiller, M.L. and Poulson, T.L. (2010)
- Niemiller, M. L., Near, T. J. and Fitzpatrick, B. M. (2011)
- Niemiller, M.L. (2011)
- Niemiller, M.L., Graening, G.O., Fenolio, D.B., Godwin, J.C., Cooley, J.R., Pearson, W.D., Fitzpatrick, B.M. and Near, T.J. (2013)
- Niemiller, M.L., Higgs, D.M. and Soares, D. (2013)
- Niemiller, M.L., Fitzpatrick, B.M., Shah, P., Schmitz, L. and Near, T.J. (2013)
- Armbruster, J., Niemiller, M.L. and Hart, P.B. (2016)
- Ponta, G.M.L., McGregor, S.W. and Jones, S.W. (2018)
- Mouser, J. (2019)
- Niemiller, M.L., Taylor, S.J., Slay, M.E. and Hobbs, H.H. III (2019)
- Hart, P.B., Niemiller, M.L., Burress, E.D., Armbruster, J.W., Ludt, W.B. and Chakrabarty, P. (2020)
- Adams, G.L., Burr, B.M. and Warren, M.L. (2020)
- Ponta, G.M.L., McGregor, S.W. and Blackwood, R. (2020)
- Ponta, G. (2020)
- Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. (2021)
- Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. (2022)
- Mouser, J. (2022)
- Niemiller, M.L., Hart, P.B., Pirro, S. and Arcila, D. (2025)
- Brownstein, C.D., Policarpo, M., Harrington, R.C., Hoffman, E.A., Stokes, M.F., Casane, D. and Near, T.J. (2025)
- U.S. Department of Interior, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Southeast Region (2025)
| Cooper, J.E. | Journal Article | 1968 | Preliminary comments on a new genus and species of cave fish from Alabama |
| Cooper, J.E. and Kuehne, R.A. | Journal Article | 1974 | Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni, a new genus and species of subterranean fish from Alabama |
| Bechler, D.L. | Thesis | 1980 | The evolution of agonistic behaviour in amblyopsid fishes |
| Cooper, J.E. | Book Section | 1980 | Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni Cooper and Kuehne Alabama cavefish |
| Bechler, D.L. | Journal Article | 1981 | Behavioral studies on the Amblyopsidae; the cave, spring and swamp fish |
| Bechler, D.L. | Journal Article | 1981 | Agonistic behaviour in the Amblyopsidae; the cave, spring and swamp fishes |
| US Fish and Wildlife Service | Journal Article | 1982 | Recovery plan dor the Alabama cavefish, Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni Cooper and Kuehne 1974 |
| U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | Book | 1982 | Gray bat recovery plan |
| Bechler, D.L. | Journal Article | 1983 | The evolution of agonistic behaviour in Amblyopsid fishes |
| Cobb, R.M. | Journal Article | 1985 | A reconnaissance of caves in Lauderdale and Colbert counties,Alabama for the Alabama cavefish Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni |
| Cobb, R.M. | Journal Article | 1986 | An attempt to collect specimens of cavefish at three cave sites in northwest Alabama |
| U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | Journal Article | 1987 | Proposed rule to reclassify the Alabama cavefish (Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni), from threatened to endangered |
| U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | Journal Article | 1988 | Reclassification of the Alabama cavefish from threatened to endangered |
| U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | Journal Article | 1990 | Alabama cavefish, (Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni) Cooper and Kuehne, 1974 Recovery plan |
| Aley, T. | Journal Article | 1990 | Delineation and hydrogeologic study of Key Cave aquifer, Lauderdale County, Alabama |
| U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | Journal Article | 1991 | Alabama cavefish (Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni) |
| U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | Report | 1994 | Draft Environmental Assessment and Land Protection Plan. Proposed establishment of Key Cave National Wildlife Refuge |
| U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | Journal Article | 1996 | Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni |
| U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service | Book | 1996 | Final environmental assessent and land protection plan. Proposed establishment of Key Cave National Wildlife Refuge, Lauderdale County, Alabama |
| Romero, A. | Journal Article | 1998 | Threatened fishes of the world: Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni Cooper and Kuehne, 1974 (Amblyopsidae) |
| Kidd, R.E., Taylor, C.T. and Stricklin, V.E. | Report | 2001 | Use of ground-water tracers to evaluate the hydraulic connection between Key Cave and the proposed industrial site near Florence, Alabama, 2000 and 2001 |
| Poulson, T. | Journal Article | 2001 | Morphological and physiological correlates of evolutionary reduction of metabolic rate among amblyopsid cave fishes |
| Kuhajda, B.R. and Mayden, R.L. | Journal Article | 2001 | Status of the federally endangered Alabama cavefish, Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni (Amblyopsidae), in Key Cave and surrounding caves, Alabama |
| Poly, WJ and Wetzel, JE | Journal Article | 2003 | Transbrachioral spawning: novel reproductive strategy observed for the pirate perch Aphredodereus sayanus (Aphredoderidae) |
| Poly, W.J. and Proudlove, G.S. | Journal Article | 2004 | Family Amblyopsdae Bonaparte 1846 |
| Kuhajda, B.R. | Journal Article | 2004 | The impact of the proposed Eddie Frost Commerce Park on Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni, the Alabama cavefish, a federally endangered species restricted to Key Cave, Lauderdale County, Alabama |
| Niemiller, ML and Fitzpatrick, BM | Journal Article | 2008 | Phylogenetics of the Southern cavefish, Typhlichthys subterraneus: Implications for conservation and management |
| Niemiller, M.L. and Poulson, T.L. | Book Section | 2010 | Subterranean fishes of North America: Amblyopsidae |
| Niemiller, M. L., Near, T. J. and Fitzpatrick, B. M. | Journal Article | 2011 | Delimiting species using multilocus data: Diagnosing cryptic diversity in the Southern Cavefish, Typhlichthys Subterraneus (Teleostei: Amblyopsidae) |
| Niemiller, M.L. | Thesis | 2011 | Evolution, speciation, and conservation of amblyopsid cavefishes |
| Niemiller, M.L., Graening, G.O., Fenolio, D.B., Godwin, J.C., Cooley, J.R., Pearson, W.D., Fitzpatrick, B.M. and Near, T.J. | Journal Article | 2013 | Doomed before they are described? The need for conservation assessments of cryptic species complexes using an amblyopsid cavefish (Amblyopsidae: Typhlichthys) as a case study |
| Niemiller, M.L., Higgs, D.M. and Soares, D. | Journal Article | 2013 | Evidence for hearing loss in amblyopsid cavefishes |
| Niemiller, M.L., Fitzpatrick, B.M., Shah, P., Schmitz, L. and Near, T.J. | Journal Article | 2013 | Evidence for repeated loss of selective constraint in rhodopsin of amblyopsid cavefishes (Teleostei: Amblyopsidae) |
| Armbruster, J., Niemiller, M.L. and Hart, P.B. | Journal Article | 2016 | Morphological evolution of the cave-, spring-, and swampfishes of the Amblyopsidae |
| Ponta, G.M.L., McGregor, S.W. and Jones, S.W. | Report | 2018 | Hydrogeological assessment of Key Cave, Lauderdale County, Alabama |
| Mouser, J. | Thesis | 2019 | Examining occurrence, life history, and ecology of cavefishes and cave crayfishes using both traditional and novel approaches |
| Niemiller, M.L., Taylor, S.J., Slay, M.E. and Hobbs, H.H. III | Book Section | 2019 | Biodiversity in the United States and Canada |
| Hart, P.B., Niemiller, M.L., Burress, E.D., Armbruster, J.W., Ludt, W.B. and Chakrabarty, P. | Journal Article | 2020 | Cave-adapted evolution in the North American Amblyopsid fishes Inferred using phylogenomics and geometric morphometrics |
| Adams, G.L., Burr, B.M. and Warren, M.L. | Book Section | 2020 | Amblyopsidae: Cavefishes |
| Ponta, G.M.L., McGregor, S.W. and Blackwood, R. | Conference Paper | 2020 | Time series hydrologic monitoring within karst aquifers of Key Cave and Cathedral Caverns, Alabama |
| Ponta, G. | Web Page | 2020 | Monitoring karst aquifers in north Alabama for the protection of sensitive aquatic biota |
| Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. | Journal Article | 2021 | Refining sampling protocols for cavefishes and cave crayfishes to account for environmental variation |
| Mouser, J.B., Brewer, S.K., Niemiller, M.L., Mollenhauer, R. and Van Den Bussche, R.A. | Journal Article | 2022 | Lithology and disturbance drive cavefish and cave crayfish occurrence in the Ozark Highlands ecoregion |
| Mouser, J. | Journal Article | 2022 | Lithology and disturbance drive cavefish and cave crayfish occurrence in the Ozark Highlands ecoregion |
| Niemiller, M.L., Hart, P.B., Pirro, S. and Arcila, D. | Journal Article | 2025 | The complete genome sequences of 12 species of Percopsiformes |
| Brownstein, C.D., Policarpo, M., Harrington, R.C., Hoffman, E.A., Stokes, M.F., Casane, D. and Near, T.J. | Journal Article | 2025 | Convergent evolution in Amblyopsid cavefishes and the age of eastern North American subterranean ecosystems |
| U.S. Department of Interior, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Southeast Region | Report | 2025 | Key Cave National Wildlife Refuge - Draft spatial habitat and species plan supplemental document and draft environmental assessment |